
Broadcom forecasts fourth-quarter revenue below Wall Street expectations
Broadcom forecast fourth-quarter revenue below Wall Street estimates on Thursday, on worries bleak enterprise spending and stiff competition
2023-09-01 04:25

More Bitcoin ETF Decisions Are Already Looming After SEC Declines to Rule
Bitcoin ETF candidates got another dose of disappointment when US regulators on Friday punted on making a decision
2023-08-13 22:16

The ‘Yield Curve’ Is Improving. These Types of Stocks Should Benefit.
Concerns about the economy aren’t completely going away, but the 10-year Treasury yield has risen substantially in the past several months.
2023-09-28 13:27
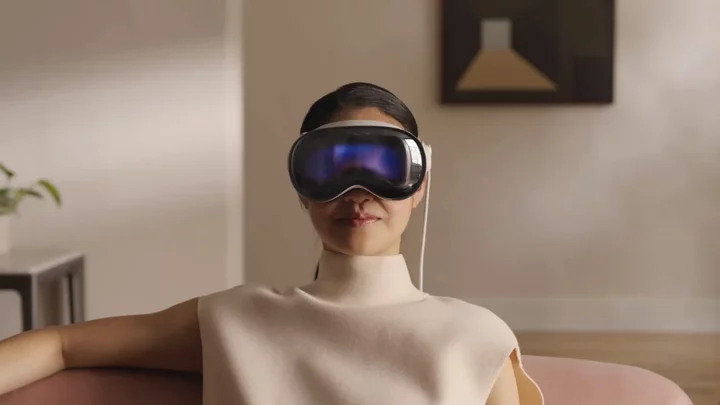

Apple's Vision Pro might be tricky to get in 2024
Apple's Vision Pro augmented reality headset hasn't even been released yet, and it's already in
2023-07-03 20:53

NBA 2K24 Replica Builds
Check out all the best NBA 2K24 replica builds for every position to dominate NBA and Park games in MyCAREER mode,
2023-09-26 04:28

FIFA 23 FUTTIES Best of Batch 2 Player Pick: How to Complete the SBC
FIFA 23 FUTTIES Best of Batch 2 Player Pick SBC is now live. Here's how to complete the SBC and the list of players you can pack.
2023-08-05 01:52
Toshiba Expands Line-up of Thermoflagger™, a Simple Solution that Detects Temperature Rises in Electronic Equipment
KAWASAKI, Japan--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 13, 2023--
2023-09-14 10:15
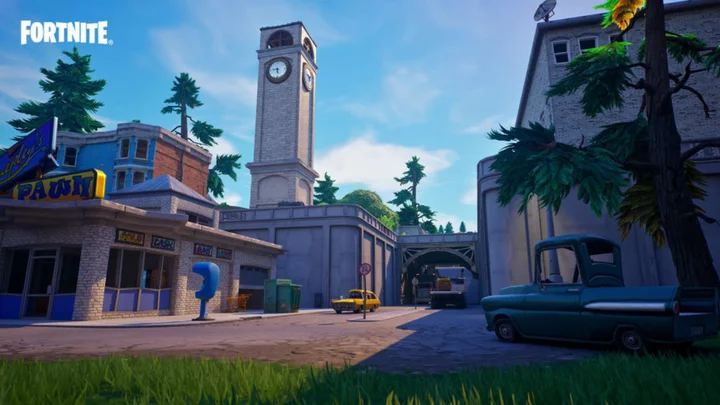

Fortnite OG Map Likely Staying in Chapter 5 As UEFN Map
New leaks claim the Fortnite OG map is likely staying in Fortnite Chapter 5 as a playable UEFN map after its recent success.
2023-11-15 02:23

Rollic Partners with Dana White’s Premier Slap Fighting Organization, Power Slap, to Launch New Mobile Game
SAN MATEO, Calif. & LAS VEGAS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 9, 2023--
2023-08-10 03:45
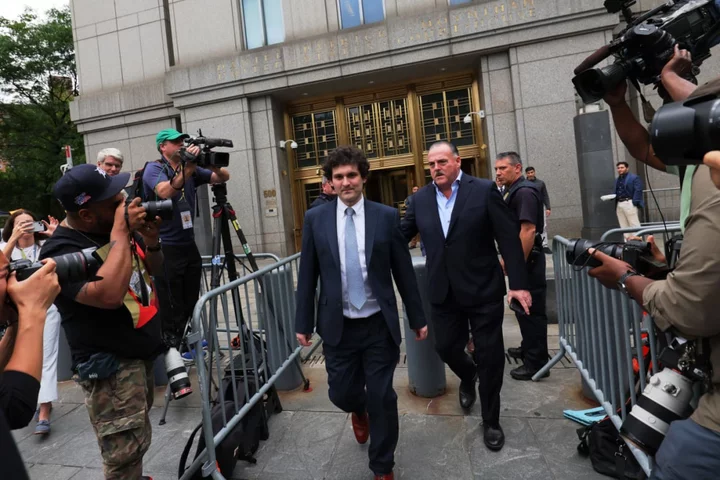

Sam Bankman-Fried’s Trial Is Is a Reminder for Crypto Traders to Be Wary
It's a reminder to investors how little recourse they have should the trading platforms they do business with go under.
2023-10-02 13:22
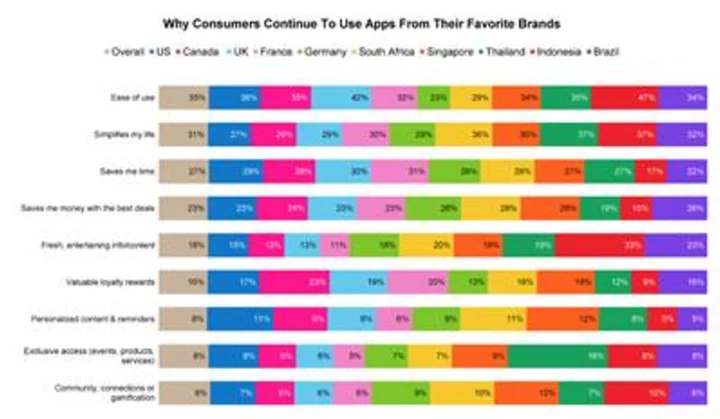
Airship Finds Most Consumers Turn to Mobile Apps to Simplify Their Lives
LAS VEGAS--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 23, 2023--
2023-05-23 21:27

Microsoft Says DDoS Attack Caused Outlook, OneDrive Service Disruption
Microsoft confirmed disruption to its Microsoft 365 apps earlier this month was due to a
2023-06-19 19:24
You Might Like...
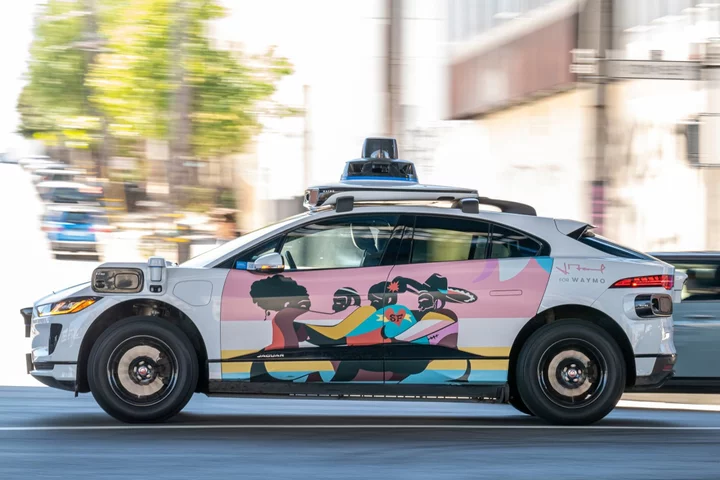

Google’s Waymo, Cruise Get Nod to Expand San Francisco Robotaxis

Water discovered leaking from Earth's crust into the planet's core

Mizkif's accidental Twitch earnings revelation sparks social media buzz while Asmongold mocks streamer's income
What is biohacking – the latest wellness trend taking over TikTok?
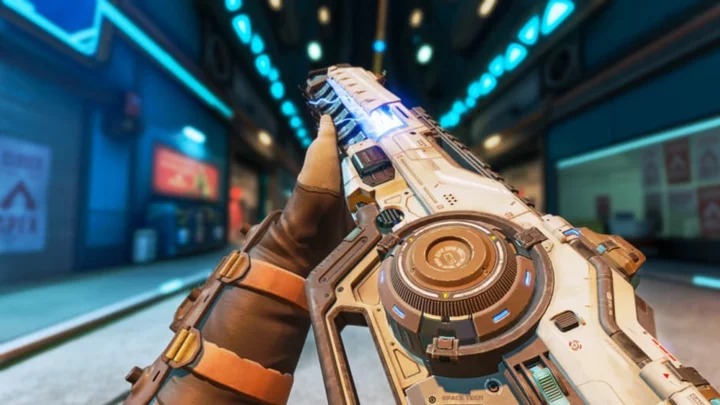

Did the Nemesis AR Get Buffed in Apex Legends?

World’s Most Valuable Chipmaker Nvidia Unveils More AI Products After $184 Billion Rally

Pokimane drops hint about returning to 'League of Legends', Internet dubs it 'worst decision ever'

Game changer: Final Fantasy's decades of reinvention
