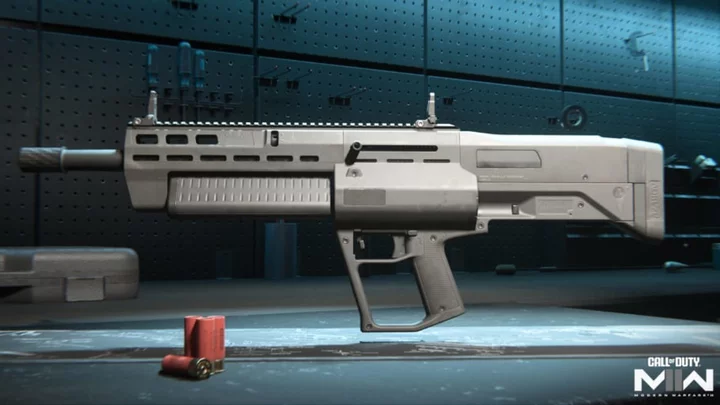

How to Unlock Dragon's Breath Rounds for the MX Guardian in Warzone 2
Players can unlock Dragon's Breath rounds for the MX Guardian in Warzone Season 4 Reloaded by changing the weapon from fully-automatic to burst mode.
2023-07-18 05:15

Banuba TINT Virtual Try-on Platform Massively Enhances Cutting-Edge Skin Care Feature
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 13, 2023--
2023-09-14 00:29

Stream everything your heart desires with an Apple TV HD for just $79
SAVE $20: As of June 1, the Apple TV HD (2nd generation, 32GB) is down
2023-06-01 22:57

BlackRock woos investors for ethereum trust to further crypto push
Asset management giant BlackRock on Thursday began courting public investors for an ethereum trust, doubling down on its
2023-11-16 21:23
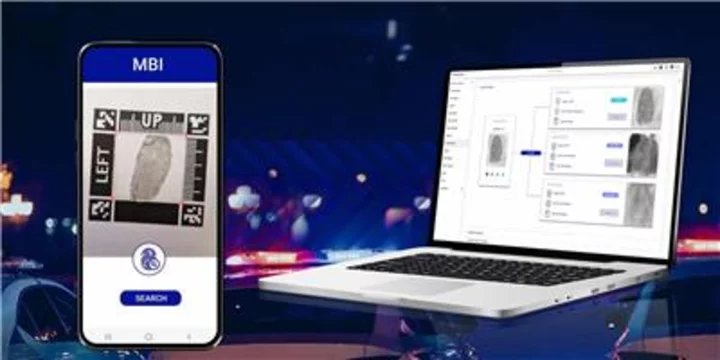
Forensic Investigation Goes Mobile With Thales
PARIS LA DÉFENSE--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 21, 2023--
2023-08-21 21:29

UN rights council calls for AI transparency
The UN Human Rights Council on Friday called for transparency on the risks of artificial intelligence and for the data harvested by...
2023-07-14 23:54

Twitter threatens to sue Meta after rival app Threads gains traction
Twitter is threatening Meta with a lawsuit after the blockbuster launch of Meta's new Twitter rival, Threads — in perhaps the clearest sign yet that Twitter views the app as a competitive threat.
2023-07-07 05:25

Spotify to lay off 200 workers in podcast division
Spotify Technology SA said on Monday it would lay off 200 employees in its podcast division, representing about
2023-06-05 20:52

Is WhatsApp down? Here's what we know.
Yes, the world's most popular messaging app, Meta's WhatsApp, was having serious issues on Wednesday.
2023-07-20 05:48

Save on a 'Star Wars Jedi: Survivor' Xbox bundle, plus more gaming deals this week
UPDATE: May. 9, 2023, 5:00 a.m. EDT This list has been updated with the latest
2023-05-09 17:56

Meta sued over ‘open secret’ of ‘pursuing’ and signing up millions of underage users
Facebook‘s parent company Meta disabled only a small fraction of the over one million reports it received of underage users on Instagram since early 2019, a lawsuit filed by 33 US states reportedly said. The newly unsealed legal complaint accused the tech giant of carrying an “open secret” that it had millions of users under the age of 13, and that Instagram “routinely continued to collect” their personal information such as location without parental permission. The complaint stated that within the company, Meta’s actual knowledge that millions of Instagram users were under the age of 13 was an “open secret” that was routinely documented, rigorously analyzed and confirmed, and zealously protected from disclosure to the public, according to a New York Times report. Last month, attorneys general from 33 states, including New York’s AG Letitia James, filed a lawsuit against Meta alleging that the tech giant designed harmful features contributing to the country’s youth mental health crisis. The lawsuit alleged Meta created addictive and “psychologically manipulative” features targeting young people while assuring the public falsely that the platform was safe to use. “Meta has profited from children’s pain by intentionally designing its platforms with manipulative features that make children addicted to their platforms while lowering their self-esteem,” Ms James said. Meta’s spokesperson responded to the lawsuit, saying that the company was committed to providing teens with “safe, positive experiences online,” and that it had already introduced “over 30 tools to support teens and their families” such as age verification and preventing content promoting harmful behaviours. “We’re disappointed that instead of working productively with companies across the industry to create clear, age-appropriate standards for the many apps teens use, the attorneys general have chosen this path,” the spokesperson added. However, a significant portion of the evidence provided by the states was obscured from public view via redactions in the initial filing. The new unsealed complaint filed last week provided fresh insights from the lawsuit, including the accusation that Instagram “coveted and pursued” underage users for years and that Meta “continually failed” to make effective age-checking systems a priority. The lawsuit reportedly argued that Meta chose not to build effective systems to detect and exclude underage teen users, viewing them as a crucial next generation demographic it needed to capture. It also accused the tech giant of “automatically” ignoring some reports of under 13 users and allowing them to continue using the platform while knowing about such cases via the company’s internal reporting channels. The company responded that the now publicly revealed complaint “mischaracterizes our work using selective quotes and cherry-picked documents.” It said verifying the ages of its users was a “complex” challenge especially with younger people who likely do not have IDs or licenses. Meta recently said it supports federal legislation requiring app stores to get parents’ approval whenever their teens under 16 download apps. “With this solution, when a teen wants to download an app, app stores would be required to notify their parents, much like when parents are notified if their teen attempts to make a purchase,” the company said. “Parents can decide if they want to approve the download. They can also verify the age of their teen when setting up their phone, negating the need for everyone to verify their age multiple times across multiple apps,” it said. The tech giant holds that the best solution to support young people is a “simple, industry-wide solution” where all apps are held to the same standard. “By verifying a teen’s age on the app store, individual apps would not be required to collect potentially sensitive identifying information,” Meta recently said. Read More Russia places Meta spokesperson on wanted list Meta to allow users to delete Threads accounts without losing Instagram Nasa has received a signal from 10 million miles away Nasa has received a signal from 10 million miles away Elon Musk set to meet Netanyahu and hostage families in Israel Elon Musk weighs in on Dublin riots claiming country’s PM ‘hates the Irish people’
2023-11-27 13:51

Sunak Seeks Biden’s Backing on AI After UK Left Out of Key Talks
Prime Minister Rishi Sunak called for global cooperation to guard against risks posed by artificial intelligence, before talks
2023-06-08 05:48
You Might Like...

China defends ban on US chipmaker Micron, accuses Washington of 'economic coercion'

What East Coast Cities Can Learn About Wildfire Policies From the West

Valorant Patch 7.09 Agent Tier List
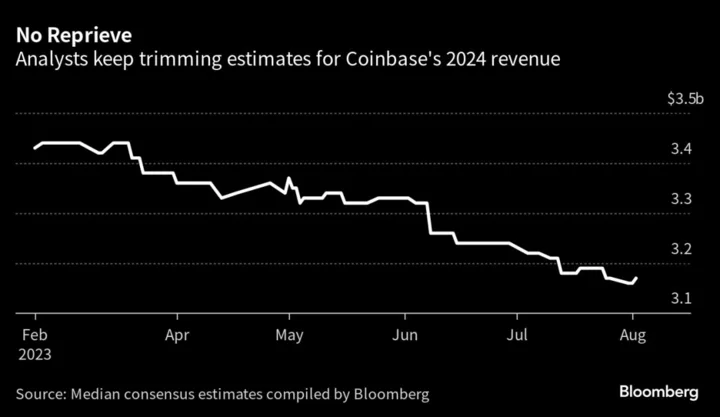
Coinbase Rally Leaves Analysts Divided on the Crypto Exchange

Fed warned Goldman's fintech unit on risk, compliance oversight -FT

QuSecure’s QuEverywhere Named 2023 Top New Product of the Year in Quantum Cybersecurity

Valorant Patch 6.10: Full List of Changes

What to expect from Apple's big MacBook Air announcement at WWDC 2023
