
MrBeast holds competition to see whether it is easier to set up physical shop or an online one, here's what he found out
In one of his recent Instagram posts, MrBeast did a competition to see which is easier to set up, a physical shop or an online one
2023-07-17 18:17

Is IShowSpeed possessed? Kai Cenat warns YouTuber as he sits in most haunted chair: 'You stupid a**'
Explore the details of what transpired in the video, the whereabouts of these two internet personalities, and the reasons behind Speed's 'possession'
2023-07-04 14:57
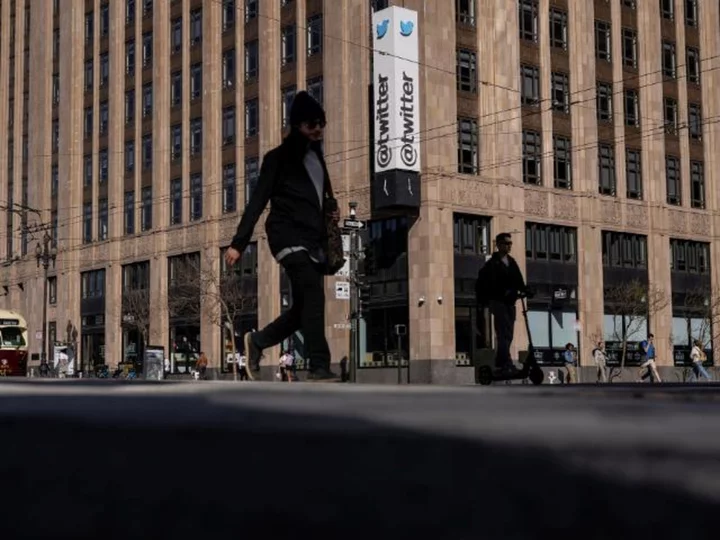

Twitter may be worth only a third of its pre-Musk value, Fidelity says
A Fidelity fund has slashed its estimate of Twitter's value amid ongoing chaos at the company, implying the social media platform may be worth only a third of its value compared to when Elon Musk acquired it in October.
2023-06-01 00:21

Nokia says will cut up to 14,000 jobs
Nokia will slash up to 14,000 jobs in a major cost-cutting drive, it said in a statement on Thursday.
2023-10-19 14:19
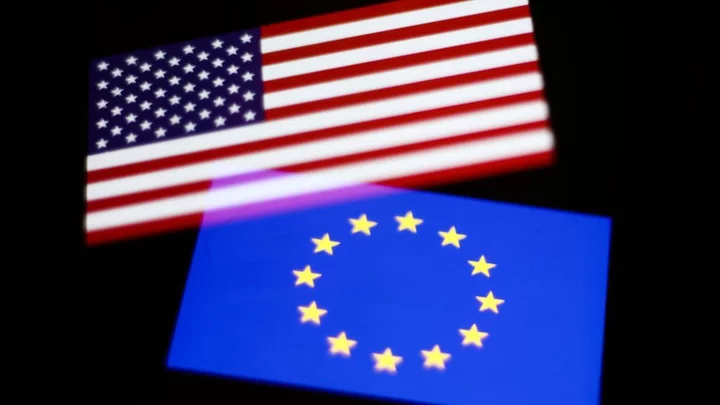

Privacy activists slam EU-US pact on data sharing
The deal overcame objections about US intelligence agencies' level of access to European data.
2023-07-11 11:25

Norway Bans Meta From Showing Users Behavioral Ads
Norway is imposing a ban on behavioral ads being shown to users of Facebook and
2023-07-17 19:56
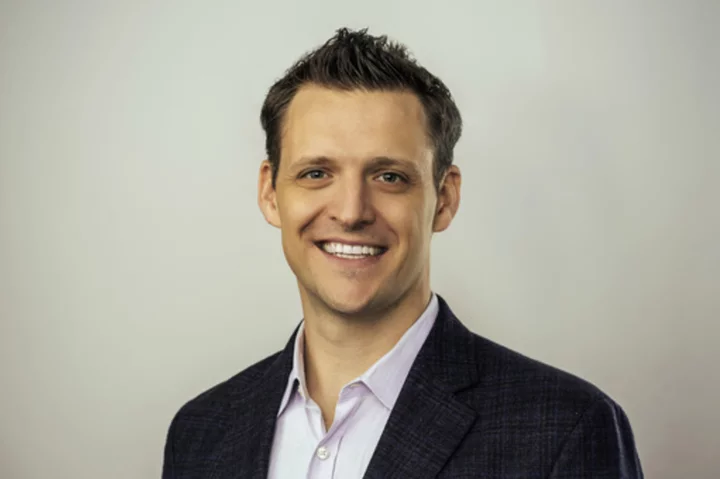

Insider Q&A: Artificial intelligence and cybersecurity in military tech
Josh Lospinoso’s first cybersecurity startup was acquired by Raytheon/Forcepoint
2023-05-29 20:24
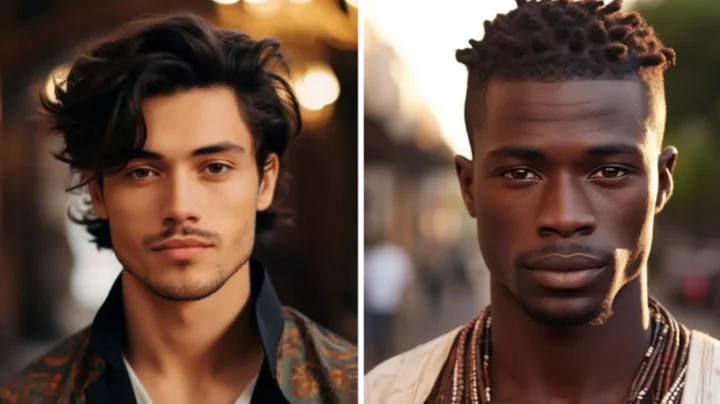

This is what the 'most attractive man' in each country looks like according to AI
Artificial intelligence has revealed what the most conventionally attractive man looks like according to the tastes of different countries. AI technology has advanced to mind-boggling capabilities, leaving many fearful for what the future may hold if it ends up in the wrong hands. But until then, others have decided to have fun with AI and use it to decipher the peak of physical attraction in men across the globe. Midjourney is a generative artificial intelligence program and it has been used to make images featuring men mostly with large muscles and chiselled jaws, representing the “Most attractive man in a country”. The reel of photos included the most attractive men in 20 different countries including, Greece, Syria, the USA and North Korea and the results were shared on the Midjourney Reddit community. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The candidate for North Korea could be seen wearing what appears to be a military uniform and had a portrait of a leader behind him. Reddit - Dive into anything from midjourney The most attractive man in the Central African Republic had dark brown skin and chest tattoos and wore lots of beaded necklaces. Some Reddit users compared the Kazakhstani man to a “Disney adaptation villain” or a “spicy Harry Styles” as the AI version resembled some of the singer’s features such as his eyes and hair. The AI-generated American man featured shoulder-lengthed light brown and blonde hair with blue eyes, a beard and big muscles. One Redditor commented: “I like how USA is literally just Chris Hemsworth lol.” Another said: “Men of Reddit take note: to be attractive you must look concerned, sincere or intense ... ideally all three at once.” Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-11 22:17

Linkwell Health Names New Chief Product Officer, Announces Expansion of Popular Targeted Engagement Solutions Product Suite
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 1, 2023--
2023-06-02 00:54

When Does Warzone 2 Shadow Siege Event End?
The Warzone 2 Shadow Siege Event ends on Aug. 21 at 1:30 p.m., giving players four more days to earn free rewards and participate in the MW3 reveal.
2023-08-18 03:18

Arduino Announces Strategic US Expansion to Serve Growing Demand for Enterprise Solutions
AUSTIN, Texas & CHICAGO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 6, 2023--
2023-06-06 19:27

Macron Says France to Channel More IMF Resources to Poor States
France will boost the volume of International Monetary Fund resources it channels back to the institution for lending
2023-06-23 16:56
You Might Like...

Logitech Named Google Cloud DEI Partner of the Year in North America

ECB Should Consider Greening Public Bond Holdings, Elderson Says

Riverbed Survey: Retention of Millennial and Gen Z Employees Rests Heavily on Digital Employee Experience– CIOs Now Becoming Chief Talent Officers Too
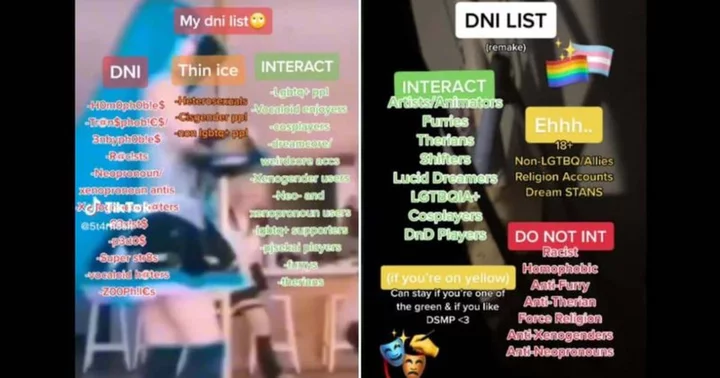
DNI: What does TikTok's latest slang mean?

Florida's feud with the College Board's AP Psychology course explained

AP, other news organizations develop standards for use of artificial intelligence in newsrooms

Clix declines Kick deal, infuriated Adin Ross says 'get out of my d**k b***h'

Capcom wants to know if more Resident Evil remakes are wanted!
