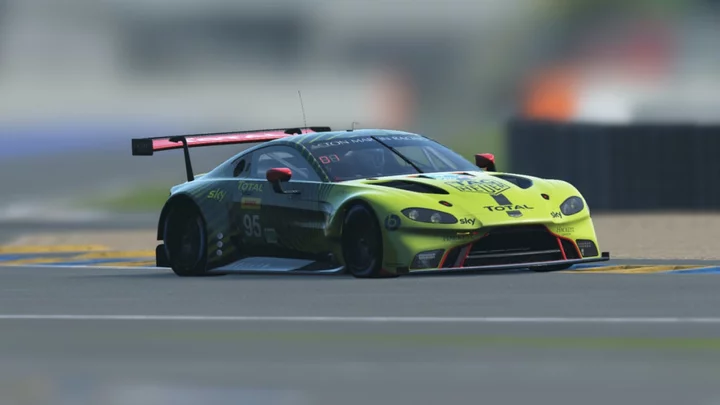
How to watch Le Mans 2023 online for free
SAVE 49%: Livestream 24 Hours of Le Mans for free with a streaming-friendly VPN. A
2023-06-07 12:28
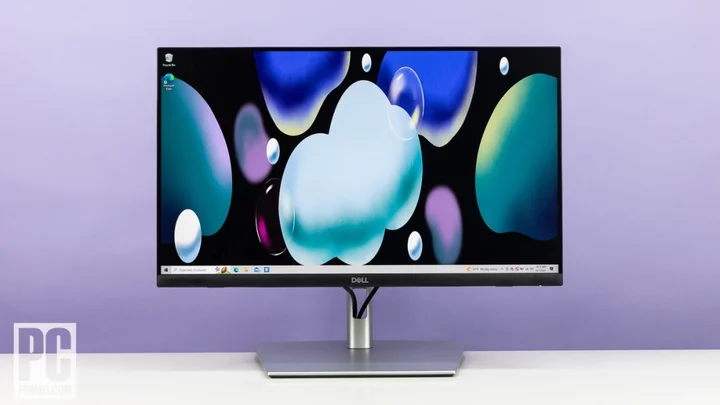

Dell 24 Touch USB-C Hub Monitor (P2424HT) Review
The Dell 24 Touch USB-C Hub Monitor (P2424HT) feels like it's two monitors rolled into
2023-09-21 07:29
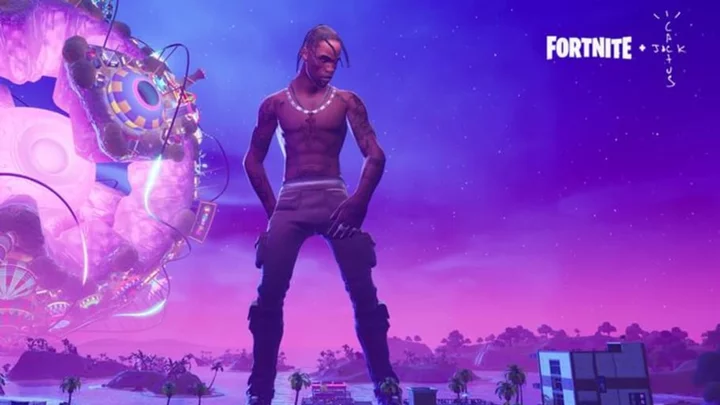

Here's When the Fortnite Festival Concert is Coming to Chapter 5
The leaked Fortnite Festival concert starts on Saturday, Dec. 9, 2023, at 9 a.m. ET in Chapter 5 with free rewards and possibly live music.
2023-11-16 23:56

Andrew Tate reports Adin Ross to Twitter’s LGBT community for controversial gender question, Internet says 'bigots are everywhere'
Controversial figure Andrew Tate and Adin Ross clashed over LGBTQ+ issues during a livestream, turning it into a heated debate on gender
2023-07-20 17:59

Grab 10% off Grubhub orders with this exclusive Amazon code
GET 10% OFF: As of June 27, existing Grubhub+ users will save 10% off orders
2023-06-28 00:51

Taiwan Mobile in Early Talks on Possible Investment in Local Crypto Platform
Telecommunications company Taiwan Mobile Co. is exploring opportunities for collaboration with local crypto platforms, including potentially investing in
2023-06-13 14:23

Boston Consulting Group Enters 40,000-ton Carbon Removal Credit Agreement with CarbonCapture Inc.
BOSTON & LOS ANGELES--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 21, 2023--
2023-06-21 15:18
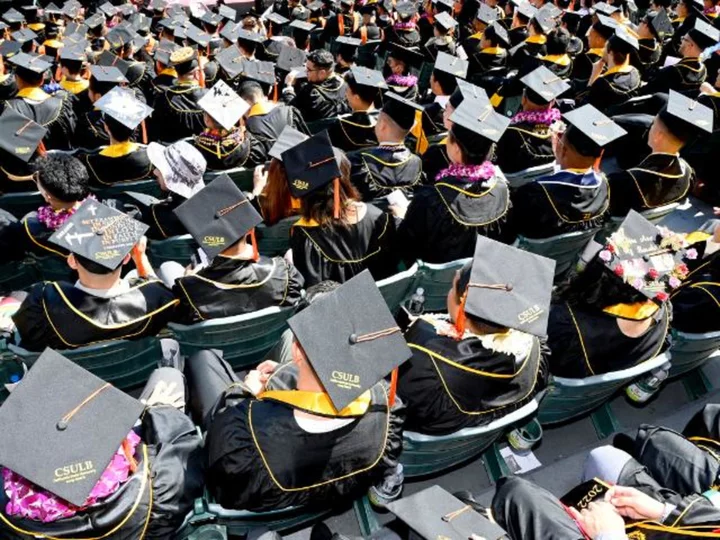

Student loan borrowers are frustrated with servicers ahead of payment restart
With less than a month before federal student loan payments restart after the years-long pandemic pause, many borrowers are having a hard time connecting with their loan servicer.
2023-09-08 22:21
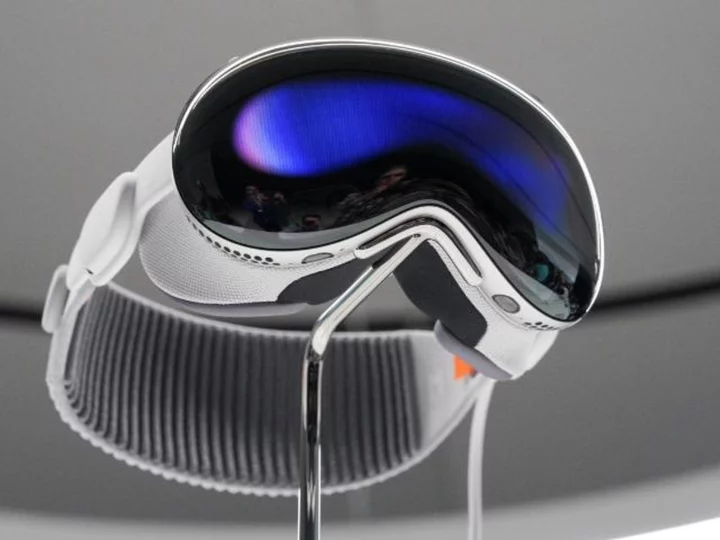

Apple's new challenge: making VR headsets look cool
When Apple unveiled its ambitious and very pricey new mixed reality headset earlier this week, executives ticked through a long list of impressive specs, teased big name partnerships and showed off a perfectly produced promo video.
2023-06-10 16:21

Barclays technology banker joins Citigroup
By Milana Vinn NEW YORK Ed Wehle, a senior Barclays Plc technology banker, has resigned to join U.S.
2023-05-17 04:22

Nvidia and Other Chip Stocks Had a Terrible September. Wall Street Remains Upbeat.
Among the 52 companies that MSCI categorizes as semiconductor makers, only Intel has avoided a share-price decline as the month draws to a close.
2023-09-29 13:52

75% of Irish data watchdog’s GDPR decisions since 2018 overruled – report
Three quarters of the Irish data watchdog’s GDPR decisions were overruled by European regulators, a report has found. The report indicates that 75% of the Data Protection Commission’s decisions in EU cases over a five-year period were overruled by the European Data Protection Board (EDPB). The EDPB had demanded tougher enforcement action in these cases, the report by the Irish Council for Civil Liberties (ICCL) said, with only one other country in one other case overruled in such a manner. The figures include final decisions from January 2023 that are not yet included in the EDPB register of final decisions, from which the figures are based. If these three cases are not included, the figure is 88% of DPC decisions overruled. The report said that the DPC tends to use its discretion under Irish law to choose “amicable resolution” to conclude 83% of the cross-border complaints it receives, instead of using enforcement measures. The ICCL report claims that Ireland remains “the bottleneck of enforcement” for major cross-border cases in Europe. “When it does eventually do so, other European enforcers then routinely vote by majority to force it to take tougher enforcement action,” it said. As Google, Meta, Apple, TikTok and Microsoft have headquarters in Ireland, the Data Protection Commission is the lead authority investigating data privacy complaints about tech giants in Europe. Some 87% of cross-border GDPR complaints to Ireland’s DPC also involve the same eight companies: Meta, Google, Airbnb, Yahoo!, Twitter, Microsoft, Apple, and Tinder. On EU-wide cases, the ICCL report found that since May 2018 – when GDPR laws came into effect – and late 2022, 64% of the 159 enforcement measures were reprimands, stating that enforcement against tech giants in Europe “remains largely paralysed”. The EDPB register of EU-level decisions shows there were 49 compliance orders issued over four and a half year years. The report called on the European Commissioner for Justice Didier Reynders to “take serious action” to enforce GDPR laws across Europe. Last summer, the Irish Government announced that two additional data protection commissioners would be hired, and that Helen Dixon would be promoted to chairwoman of the DPC – in an attempt to better resource the watchdog in recognition of its growing workload. The DPC has been carrying out a review of its governance structures, staffing arrangements and processes since last summer. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Kate Winslet calls on Government to ‘criminalise harmful content’ Humans could be controlled by robots, AI firm’s founder warns AI pioneer warns UK is failing to protect against ‘existential threat’ of machines
2023-05-15 17:28
You Might Like...

Microsoft, Activision CEOs to Defend $69 Billion Deal in Fight With FTC
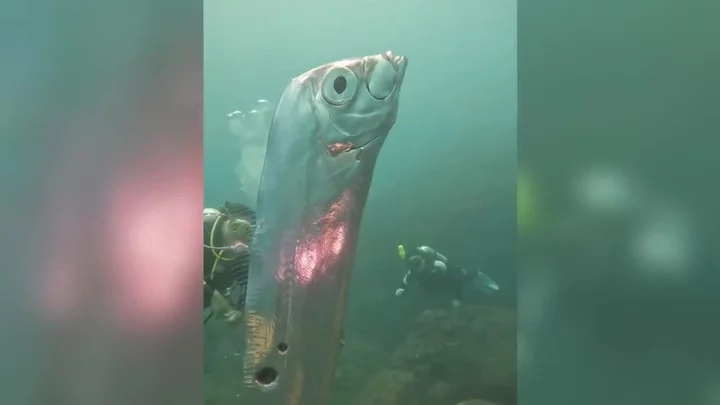

Rare six-foot fish sighting sparks ‘doomsday’ theories

Exclusive-Amazon has drawn thousands to try its AI service competing with Microsoft, Google
Become an Insider: How to Check Out Early Versions of Windows

Chemify Announces $43 Million of Funding to Digitize Chemistry

BlackRock Taps Private Debt Market With New Transition Fund

TSMC Sales Ride AI Demand Boost to Beat Estimates

xQc buys nearly $45K diamond-studded Audemars Piguet watch for JesseSMFI, fans joke 'Adept needs 50% of that'
