
Paralysed man walks again via thought-controlled implants
A paralysed man has regained the ability to walk smoothly using only his thoughts for the first time, researchers said on Wednesday, thanks to two implants that restored...
2023-05-24 23:59
Georgia school board fires teacher for reading a book to students about gender identity
A Georgia school board has voted to fire a teacher after officials said she improperly read a book on gender fluidity to her fifth grade class
2023-08-18 09:57
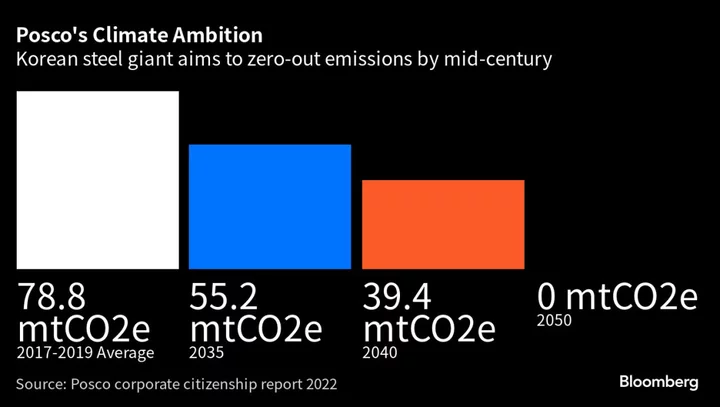
Green Steel Challenges Could Trigger Overseas Push for Posco
Posco, one of the world’s top steelmakers, would need to consider moving some of its most energy-intensive manufacturing
2023-09-25 10:16
EDITED Draws on Big Brand Expertise to Launch myEDITED
LONDON & NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 19, 2023--
2023-09-19 16:29
Ed Balls first Threads post is exactly what you expect
Just when we think we’ve found the best first post on Threads, Instagram’s new “civil” text-based app to rival Twitter, another one comes along which is miles better – and former Labour MP Ed Balls may be the all-out winner after posting exactly what you would think he would post. Well-known for his 2011 Twitter blunder in which he tweeted out his own name instead of searching for it, the Good Morning Britain presenter and ex-shadow chancellor now marks the iconic moment every 28 April on ‘Ed Balls Day’. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Now, adhering to the politician’s principle of giving the people what they want, Mr Balls has set up an account on Threads and kicked things off by posting those two magic words. And it’s fair to say other users on the platform absolutely loved it. One declared: “You’ve won Threads today!” “Thread Balls,” quipped another. A third replied: “I think you win the internet today.” Others, though, have questioned what this means for marking the special occasion, seeing as the Twitter mishap occurred on 28 April (as mentioned previously), but this more deliberate posting happened on 6 July. “Ed! Now I need to rearrange my whole calendar for a new holiday,” complained one user. A second jokingly fumed: “Who do you think you are, Ed? The monarch? You don’t get two special days.” Another asked if the post marked “the new Ed Balls Day”, but that question remains unanswered. It’s unknown whether his wife Yvette Cooper MP, the shadow home secretary, will replicate the meme by reposting one of her Twitter typos. She does have a Threads account, at least… Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-07 17:21

Do Kai Cenat and IShowSpeed 'regret' joining Rumble? Adin Ross claims platform is 'renting their f**king streamers'
Adin Ross expressed that he believes Kai Cenat and IShowSpeed would come to regret their decision to join Rumble
2023-06-05 14:23

Belarus Group to Kick-start Zimbabwe Carbon Exchange, Zuma Says
The Belarus African Foreign Trade Association has allocated 2 million carbon credits to initiate trade in the offsets
2023-07-07 18:24
Performance Over Fidelity: How to See Your Frames Per Second (FPS) in Games
High fidelity graphics vs. performance: What do you value most in a video game? If
2023-06-15 02:22
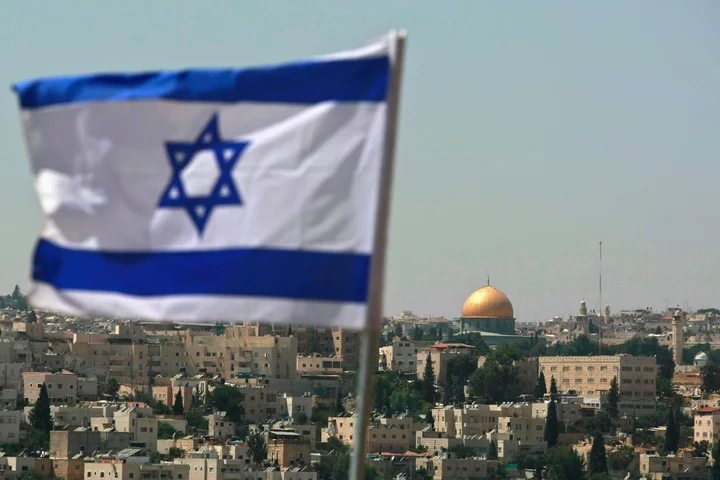

Israel Illegally Storing Millions of People’s Photos, Audit Says
Israel’s immigration authorities are illegally storing millions of photos of citizens and foreign nationals, according to a government
2023-05-16 21:29

Marketmind: Edgy market calm after worst day of 2023
A look at the day ahead in U.S. and global markets by Mike Dolan Punch-drunk from a bombardment of central
2023-09-22 18:58
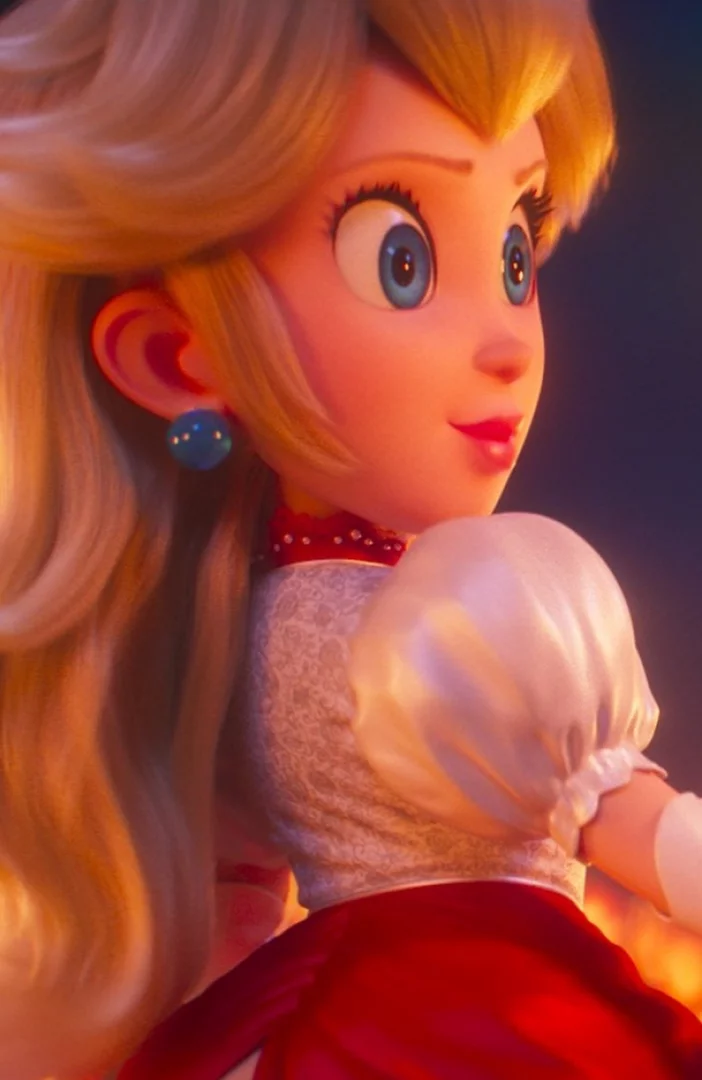

Nintendo confirms Princess Peach game
Nintendo has announced a new game focus on Princess Peach.
2023-06-22 19:22

Salem Media Announces New Podcast with Ben Taatjes and Jerrid Sebesta on the Senior Resource Podcast Network
IRVING, Texas--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 20, 2023--
2023-07-20 21:23
You Might Like...
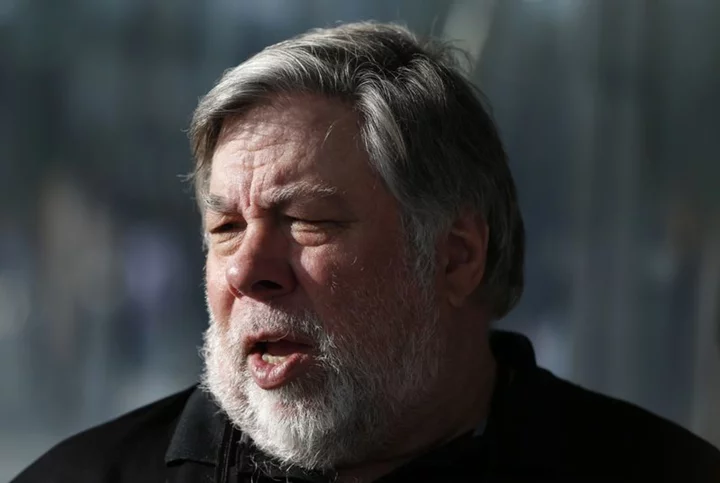

Apple co-founder Wozniak suffers possible stroke in Mexico -local media
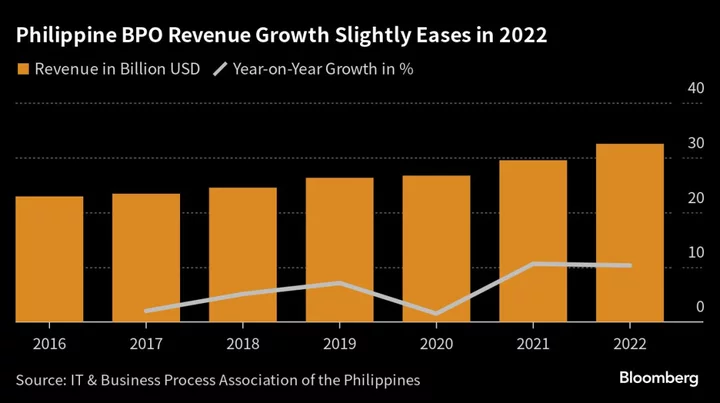
AI, Talent Shortage Pose Dual Threat to Philippine Call Centers
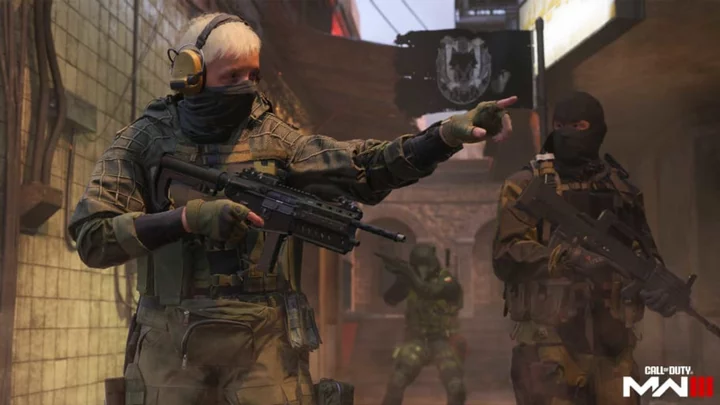

How to Get Free Double XP and Rare Camos in MW3

A new instant payment system may be coming to a bank near you

Intel Risks Being Left Behind as Nvidia Ups AI Lead

Tesla to deliver Cybertrucks after Musk tempers expectations
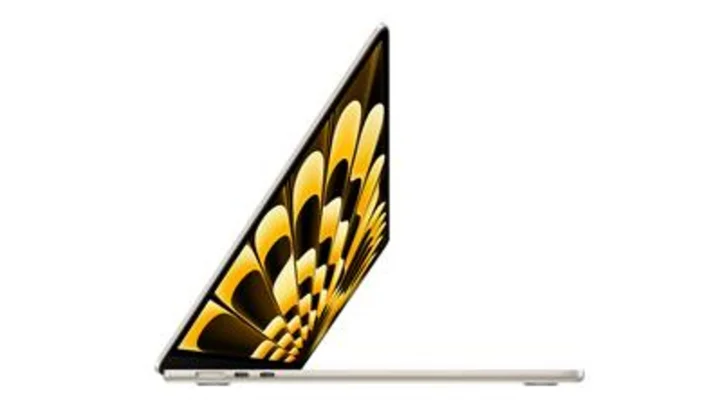

Apple introduces the 15-inch MacBook Air

Quotes: Here's what people are saying about Alibaba's management reshuffle
