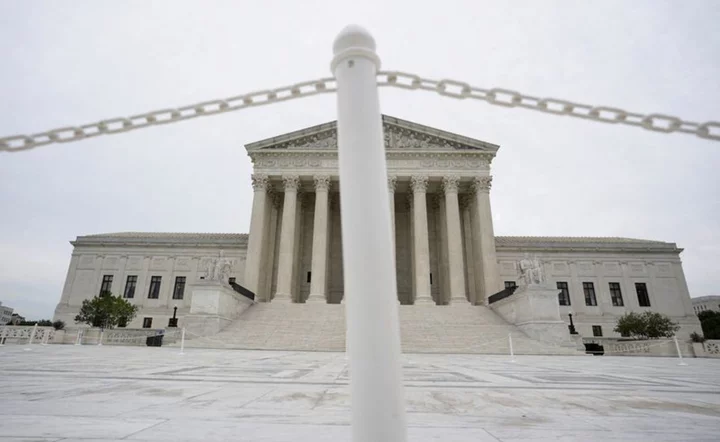

U.S. Supreme Court asked to hear high school admissions case concerning race
By Nate Raymond A parents group backed by a conservative legal organization asked the U.S. Supreme Court on
2023-08-22 11:24
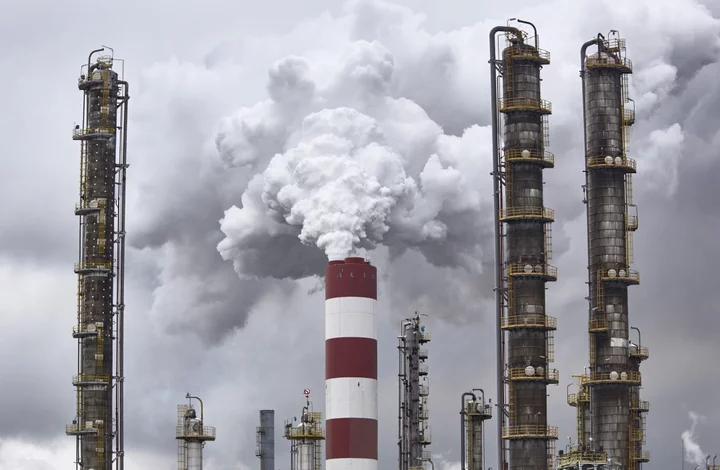

ECB Threatens 20 Banks With Fines for Mismanaging Climate Risk
The European Central Bank has written to about 20 lenders to warn them that it will impose fines
2023-11-22 15:18

Microsoft Is Working on PC Game Streaming for Game Pass Subscribers
Internal emails reveal that Microsoft is planning to stream PC games to Game Pass subscribers
2023-09-19 00:18
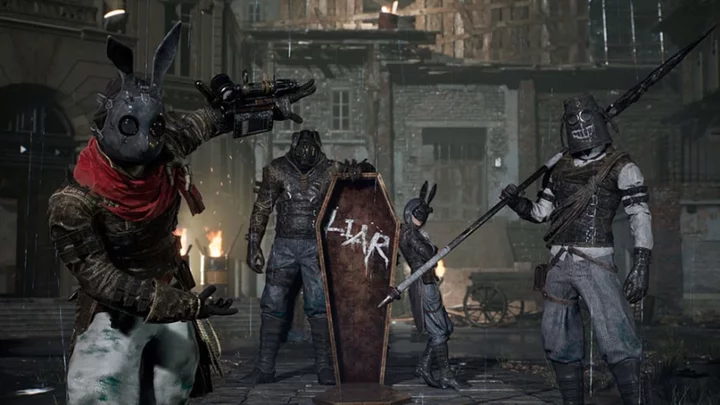
Lies of P Countdown
Here's what you need to know about Lies of P's release.
2023-08-25 04:47

Aussie telecom firms Telstra, TPG will not appeal block of asset transfer deal
Australian telecom firms Telstra Group and TPG Telecom on Monday said separately they would not appeal the country's
2023-08-14 07:26

Reddit goes dark: Why are thousands of the world’s most popular forums shutting down?
Most of Reddit has now gone “dark” in protest against the management of the online forum. The controversy began when Reddit announced that it would start charging for access to its API, the technology that allows other developers access to its data. Some of those developers immediately announced that the pricing was so high that it would make their apps unsustainable – and one, widely-respected client Apollo, has since said it will have to shut down. That set off outrage across Reddit. While that initially focused on the decision to start charging for access to its data, it has since grown, with many users suggesting that they are generally dissatisfied with the way the site is being managed. What has happened to Reddit? On June 12, many of the world’s biggest subreddits went “dark”. That meant setting their privacy settings to private, so that only anyone who is already a member can see them. For anyone who tries to visit those forums and is not a member – which includes most of those on Reddit, including many of its biggest – they will see a message that it has gone private and is therefore not available. In a widely circulated message explaining the outage, users explained that it was intended as a protest. Some will return on 14 June, after 48 hours of darkness, it says, but others might opt to never come back again if the problem is not addressed. That is because “many moderators aren’t able to put in the work they do with the poor tools available through the official app” the message reads. “This isn’t something any of us do lightly: we do what we do because we love Reddit, and we truly believe this change will make it impossible to keep doing what we love.” Why did Reddit change its policy? All of this began because Reddit announced that it would start charging for access to its API. Many of its users – including Christian Selig, the developer of the Apollo app that is at the centre of much of the controversy – say that this is reasonable. Reddit’s data is used by sites such as Google and to train artificial intelligence systems, for instance. And at the moment, Reddit is not paid for that usage, despite the fact that it costs the company (which is not profitable) to host that data. But it was the pricing and the way it was rolled out that caused such controversy. Mr Selig said that the pricing would cost his app $2 million per month, which is much more than storing the user data is thought to cost Reddit, and he and others were given only 30 days to respond. Which Reddit forums are part of the blackout? Almost all of them. The latest numbers suggest that 7259, out of 7806, of the site’s subreddits are currently unavailable to the public. Of the seven subreddits that have more than 30 million subscribers, all but one – r/pics – have been made private. A full, live list that shows both the subreddits that are down and the overall impact of the protest can be found on this tracking page. How can this happen? Reddit is unusual among social networks in that it depends heavily on its users, who administer the forums and moderate the content that appear on them. That saves it a lot of money – Meta, for instance, spends vast sums on ensuring that problematic content does not appear on Facebook and Instagram – and means that those users feel as if they should be listened to when it comes to such issues. It also means that they are able to take decisions that the management of Reddit might not like them to, including turning those subreddits private. Some 30,000 moderators are thought to be running the subreddits that are involved in the protest, and working together has given them considerable power to grind the site to a halt. Read More Reddit down amid major protest Popular Reddit app Apollo shuts down as site’s users revolt against it Millions of Reddit users face a blackout over pricing revolt Elon Musk refuses to pay Twitter’s Google bill, leaving site in peril Apple’s headset is not the most important thing it announced this week Mark Zuckerberg reveals what he thinks about Apple’s headset – and it’s not good
2023-06-13 02:22

GlobalLogic Acquires Sidero, a Leading Software Engineering Firm in Ireland
SANTA CLARA, Calif. & ATHLONE, Ireland--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 10, 2023--
2023-07-10 16:46

UK focuses on transparency and access with new AI principles
By Paul Sandle LONDON (Reuters) -Britain set out principles designed to prevent generative AI models like ChatGPT from being dominated
2023-09-18 19:23
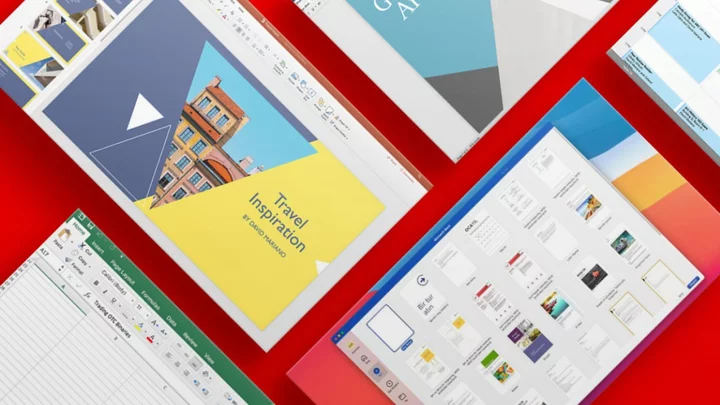
Save 86% on a lifetime license to Microsoft Office Professional for Windows
TL;DR: A lifetime license to Microsoft Office Professional for Windows is on sale for £23.70,
2023-07-04 12:29

Eerie clip showing just how deep the ocean is has left people with the creeps
A graphic video showing just how deep the ocean really goes is giving people the creeps. Posted on YouTube by MetaBall Studios, the video keeps going down and down in the water, to the likes of the Titanic wreck (which sits at 3700m below the surface), and even the level at which Mount Everest would be completely drowned. However, it has nothing on the Pacific Ocean's Challenger Deep (the deepest part of the ocean), which is around 11,000m down. Scary stuff. Click here to sign up for our newsletters
2023-06-05 18:17

Is Madison Beer joining Kick? Adin Ross says 'anybody you see on Twitch, we're working on it'
In the past, Adin Ross has claimed to offer Kick deals to other content creators and even said that they won't be paid if they turn it down
2023-06-19 19:17
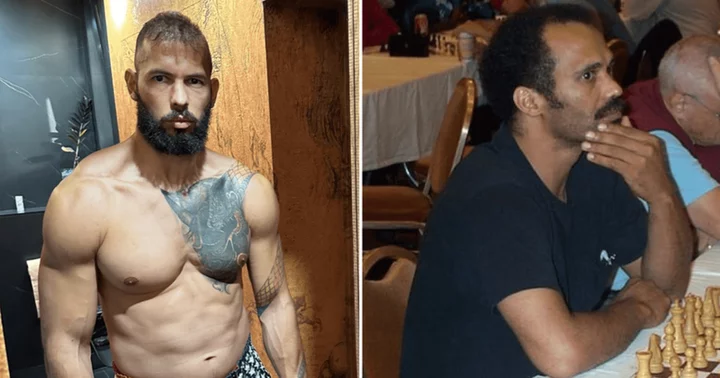
Andrew Tate claims his father's bad spelling misled AI bots into thinking he was 'crazy', trolls say 'even secret service dads don’t text like that'
Andrew Tate acknowledged that his dad often misspelled words and used poor grammar in his emails and Facebook messages
2023-07-30 19:48
You Might Like...
ECM Wins 2023 IDEA Awards for its PrintStator Electric Motor CAD Software

CDL Major 5: 3 Storylines to Follow

Astrologer explains why you might be feeling a little 'odd' at the moment

WhatsApp now lets you send videos in HD
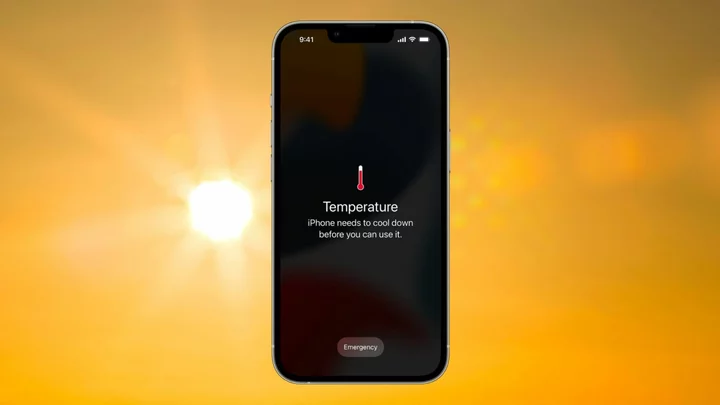
How to keep your iPhone from overheating and avoid permanent battery damage

BNP Paribas Exits Bond Arranging for New Oil, Gas Ventures

Diablo IV makes $666m less than a week after its launch

Little Nightmares III: Everything We Know So Far
