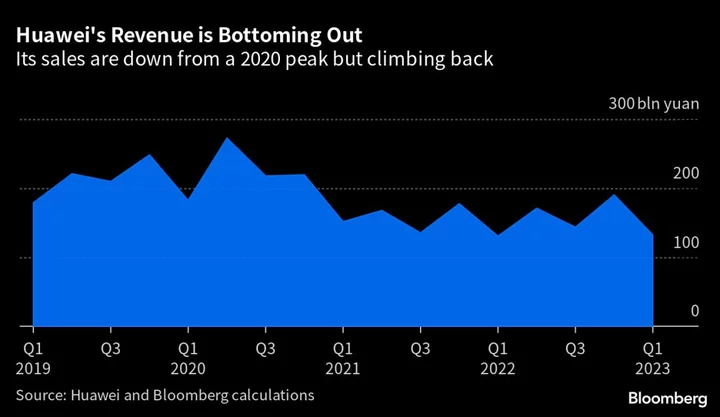
EU Takes Tougher Stance on Huawei as China Tensions Rise
The European Commission is increasing the pressure on member-nations to stop using Huawei Technologies Co. and ZTE Corp.
2023-06-16 15:57

Toyota's profits rise as global chips supply crunch subsides
Toyota’s January-March profit has edged up 3% from the previous year on robust sales as a chips supply crunch gradually eased
2023-05-10 16:54

Breakthrough solar system outperforms military-grade diesel generator
Solar panels combined with next-generation batteries now outperform military-grade diesel generators, according to new analysis. Researchers at the US Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that the novel clean energy solution was both cheaper and more reliable than its fossil fuel-powered counterpart. Tests of the two systems were carried out in accordance with the US Department of Defense’s requirements to sustain critical electric loads during a power outage over a 14-day period. The solar systems proved to have a higher resilience and lower cost compared to the diesel-based systems that are currently used, while also being less vulnerable to interruptions in the diesel supply. The researchers also highlighted the net present value (NPV) of the solar storage system, meaning it pays for itself in the long term. “The diesel-fuel-free LDES system outperforms the traditional diesel-based system and provides a large net saving that can be used to pursue third-party financing,” the researchers noted. “The continued rapid decline in photovoltaic (PV) costs allows for utility-scale PV to be economically attractive at many locations. These declines are expected to continue, which will further increase the positive NPV in the future.” The tests were performed on three separate military bases, using an innovative carbon-based battery rather than the more expensive lithium-ion batteries that are typically found in such renewable energy storage systems. The batteries tested in the experiments were Antora Energy’s battery energy storage system (BESS), which the researchers warned were not yet ready for full-scale deployment. The results of the study, however, mean decision makers are already anticipating their roll out. Michael McGhee, the Acting Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense, described the new system as “the most likely way to easily and simply generate power without the need for off-base supply chains”. The results of the research were published in a study, titled ‘Long-duration energy storage: resiliency for military installations’. Read More Solar panel advances will see millions go off grid, scientists predict
2023-11-13 19:49
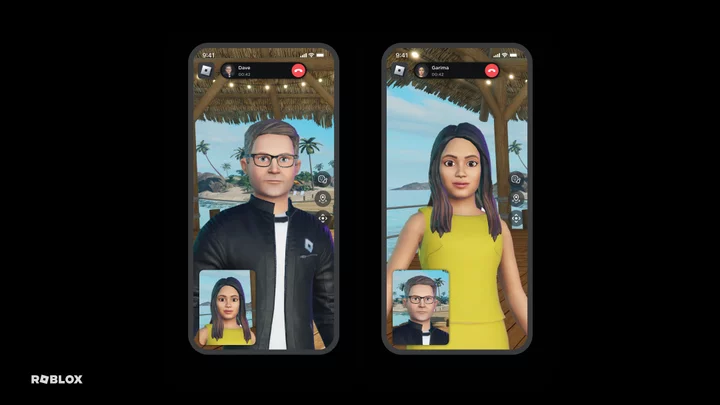

Roblox will soon let players make calls from inside the game
At the gaming giant's annual Developers Conference today (Sept. 8), Roblox announced that a new
2023-09-09 02:23

AiM Future Successfully Closes Series A Round of Investment
SAN JOSE, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 7, 2023--
2023-07-08 05:46
The Best SSDs for PS5 in 2023
One compelling feature of the Sony PlayStation 5 is its M.2 slot, which accommodates a
2023-11-16 06:53
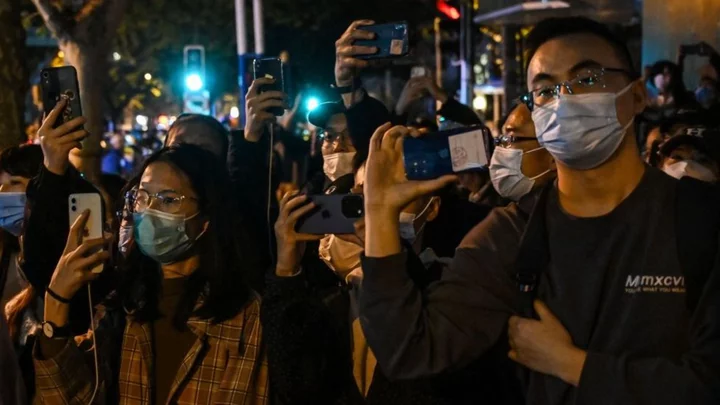

Chinese censors take aim at AirDrop and Bluetooth
Authorities are relentlessly plugging the "cracks" in China's Great Firewall to quench dissent.
2023-06-09 05:52

Apex Legends Firing Range Gets Assassin’s Creed Easter Egg
The Apex Legends developers have added a sneaky reference to Assassin's Creed in the game's firing range for eagle-eyed players.
2023-05-12 23:18

PPG introduces PPG LINQ Color software and PPG MAGICBOX body shop assistant for the refinish industry
PITTSBURGH--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 30, 2023--
2023-08-30 21:20
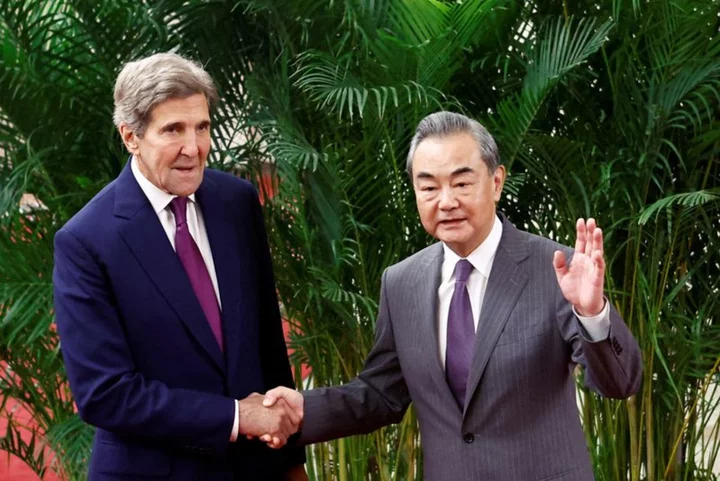

US envoy Kerry says climate cooperation could redefine US-China ties
By Valerie Volcovici BEIJING China and the United States could use climate cooperation to redefine their troubled relationship
2023-07-18 13:16

CleanMyMac Review
Most antivirus companies that publish macOS antivirus tools started with Windows security products. Not Kyiv-based
2023-07-22 15:56
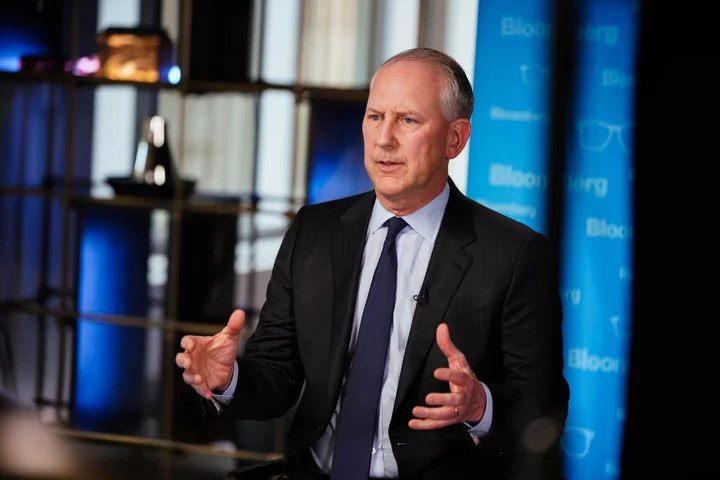

AIG’s CEO Sees Pandemic, Wars and Climate Change Among Biggest Risks
American International Group Inc. Chief Executive Officer Peter Zaffino said the biggest challenge to the insurance sector over
2023-10-20 02:58
You Might Like...
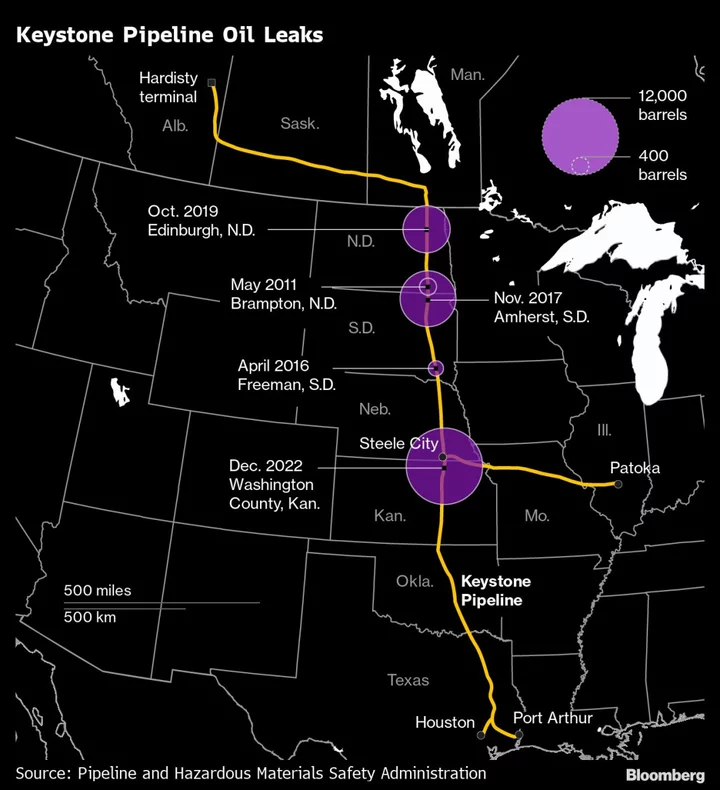
A Pipeline Pushed to the Limit Preceded Keystone’s Worst Oil Spill

Factbox-Makers of EVs, chargers adopt Tesla's charging standard

Did Richard Simmons wear a headband? History confuses fans of famous fitness instructor
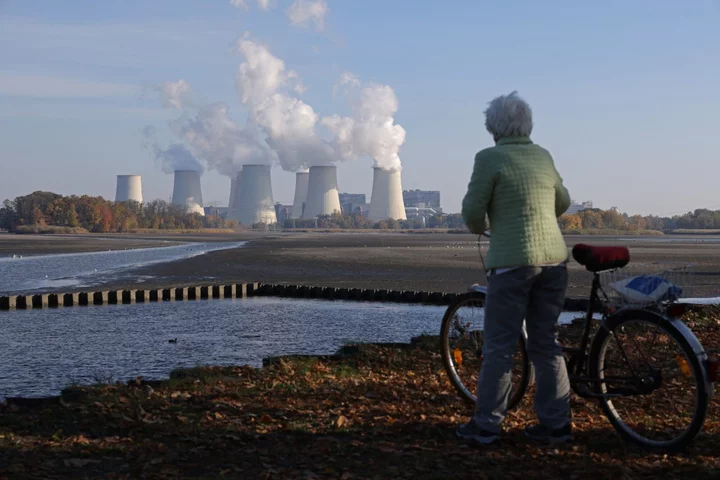

European Nations Join Island States in Calling for Fossil-Fuel Phaseout

Dillon Danis reiterates claim he has NSFW pics of Nina Agdal that could 'break Internet'

China's Tencent reports jump in Q2 income, misses revenue expectations
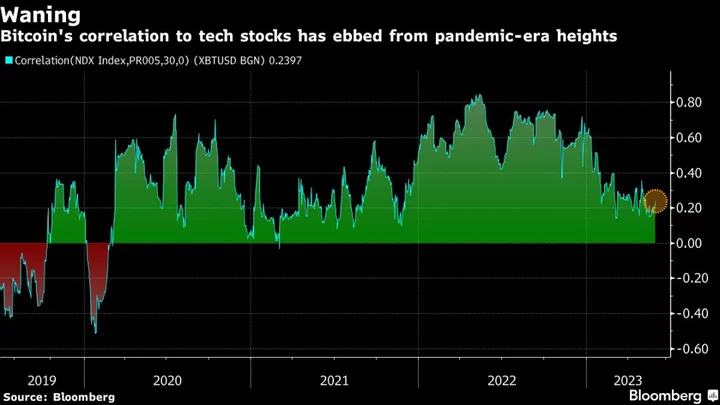
Crypto Rues Bitcoin’s Decoupling From AI-Fueled Tech Stock Gains

Get TP-Link WiFi mesh routers for $50 off at Amazon
