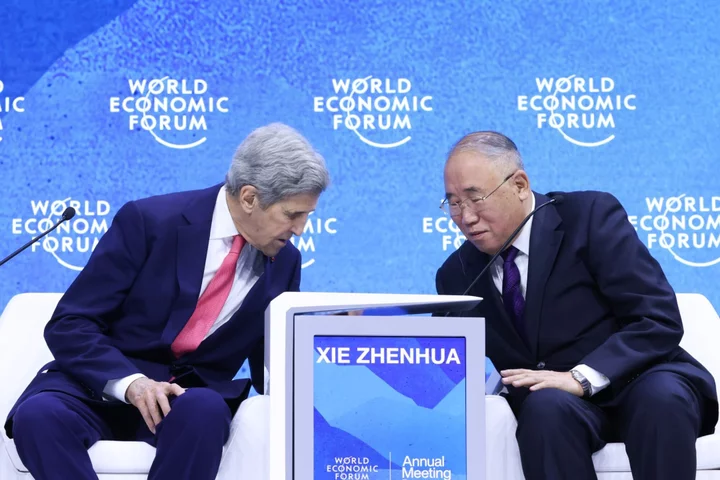

John Kerry to Visit China in Bid for Progress in Climate Crisis Talks
US Climate Envoy John Kerry is heading to China for talks on global warming as tensions simmer between
2023-07-07 05:21

GE HealthCare gets $44 million grant to develop AI-assisted ultrasound tech
GE HealthCare Technologies Inc has received a grant of more than $44 million from the Bill & Melinda
2023-09-18 20:45

Apple could be about to make the biggest change to the iPhone in 11 years
Apple is set to unveil the iPhone 15 in just a few days, and it's widely expected to come with a significant change.
2023-09-08 21:54

Need a New Look? How to Change Your iPhone Wallpaper
Looking for the right wallpaper for your iPhone? Apple offers a variety of options to
2023-08-14 23:16

'Diablo IV' is almost here. What to know about the video game's coming release
The release of “Diablo IV” is right around the corner
2023-06-02 02:26

US alleges Google got rich because people stick with search defaults
By Diane Bartz WASHINGTON The Justice Department will press its argument Thursday that Google sought to strike agreements
2023-09-14 22:46

Indonesia Delays Investment Plan for $20 Billion Climate Deal
Indonesia has delayed the launch of a much-anticipated investment plan to support a landmark $20 billion climate financing
2023-08-16 16:57

Asana Appoints New Chief Revenue Officer, Ed McDonnell
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 8, 2023--
2023-08-08 21:28

Matter Wins Four Awards at the 55th Annual Bell Ringer Awards Ceremony
BOSTON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 13, 2023--
2023-06-13 20:50

Study finds popular accessory actually likely makes ‘no difference’ to sleep quality or eye health
Special glasses marketed to filter out blue light likely do not make any difference to sleep quality or eye strain from computer use, according to a new review of studies. Blue-light blocking spectacles have been increasingly recommended, often by optometrists, since the early 2000s. Eye patients are frequently prescribed these lenses in many parts of the world with a range of marketing claims existing about their potential benefits. Some of these claims include that the special glasses may reduce eye strain associated with digital device use, improve sleep quality, and also protect the retina from light-induced damage. However, researchers, including those from the University of Melbourne in Australia, say there is “substantial debate” about whether blue-light filtering spectacle lenses have merit in ophthalmic practice. The research, published in the journal Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, assessed data from 17 clinical trials on the benefits offered by these glasses for improving visual performance, providing protection to the retina, and improving sleep quality. The review assessed data from individual studies from six countries, each including five to 156 participants, and the period of time over which the lenses were assessed ranging from less than one day to five weeks. Researchers found that there may be “no short-term advantages” with using blue-light filtering spectacle lenses to reduce visual fatigue associated with computer use, compared to non-blue-light filtering lenses. They say it is also currently unclear whether these lenses affect vision quality or sleep-related outcomes. The research review could also draw no conclusions about any potential effects on retinal health in the longer term. “People should be aware of these findings when deciding whether to purchase these spectacles,” study co-author Laura Downie said. “Our findings do not support the prescription of blue-light filtering lenses to the general population. These results are relevant to a broad range of stakeholders, including eye care professionals, patients, researchers and the broader community,” Dr Downie added. However, scientists said the quality and duration of the individual studies part of the review also needs to be considered. “High-quality, large clinical research studies with longer follow-up in more diverse populations are still required to ascertain more clearly the potential effects of blue-light filtering spectacle lenses on visual performance, sleep and eye health,” Sumeer Singh, another author of the study, said. The potential mechanisms by which these lenses might help with eye strain, sleep, and protecting the retina are also unclear, scientists say. “The amount of blue light our eyes receive from artificial sources, such as computer screens, is about a thousandth of what we get from natural daylight,” Dr Singh said. “Filtering out higher levels of blue light would require the lenses to have an obvious amber tint, which would have a substantial effect on colour perception,” he added. But the new research did not find any consistent reports of adverse side effects from using blue-light filtering lenses. Read More A bed bugs epidemic is sweeping the UK – this is why AI can predict Parkinson’s subtype with up to 95% accuracy, study suggests The return of schedules: How parents can make the most of back-to-school energy
2023-08-18 14:28
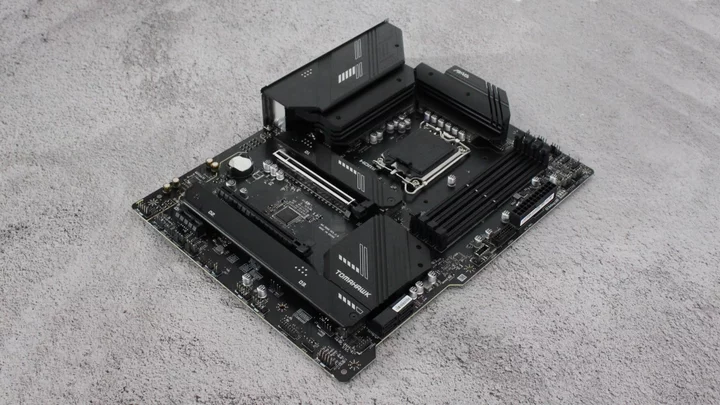

MSI MAG B760 Tomahawk Wi-Fi Review
The MSI MAG B760 Tomahawk Wi-Fi ($219.99 MSRP; often $199 or less on sale) is
2023-07-23 13:45

Google's Bard AI chatbot is vulnerable to use by hackers. So is ChatGPT.
Bard, Google's entry in the chatbot race, is meant to compete with the AI juggernaut
2023-07-15 03:21
You Might Like...

A $239 Million Climate Tech Fund for Startups With Overlooked Carbon Solutions
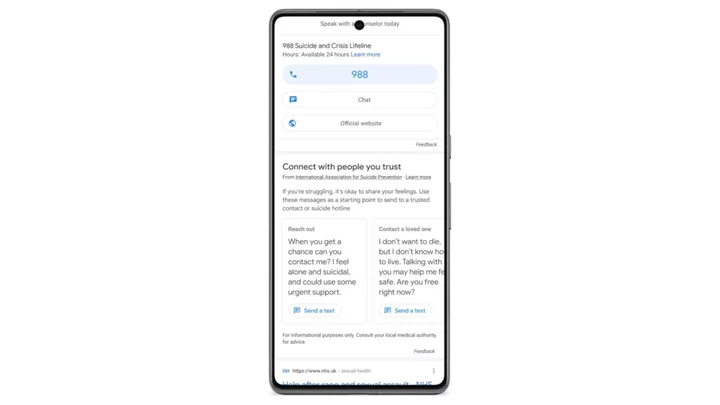
Suicide-related Google searches will provide message templates for reaching out

Hawaii officials seek families help in identifying remains of wildfire victims

China-US climate progress could hinge on curbing of methane
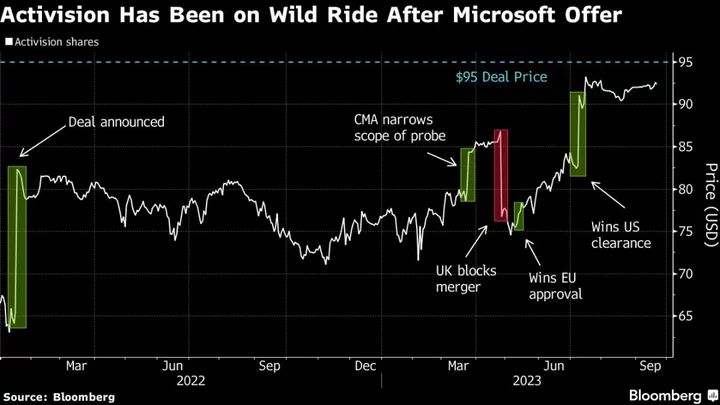
Activision Nears Microsoft Offer Price as UK Approval Pends

Assassin’s Creed: Mirage to drop 7 days early

Royal website subject to ‘denial of service attack’, royal source says

KinderCare announces Champ Camp: Adventure Edition
