
BP Chief’s Surprise Exit Leaves Questions Over Green Strategy
The abrupt resignation of BP chief Bernard Looney marks the loss of an executive who pushed for a
2023-09-13 10:46

Ondine Biomedical Appoints Senior Pharma Executive Dr. Simon Sinclair as Chief Medical Officer
VANCOUVER, British Columbia--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 1, 2023--
2023-06-01 21:50

Elon Musk's X/Twitter is letting paying users hide their blue ticks
Back when blue ticks on Twitter were something you had to apply for, they were
2023-08-02 17:45
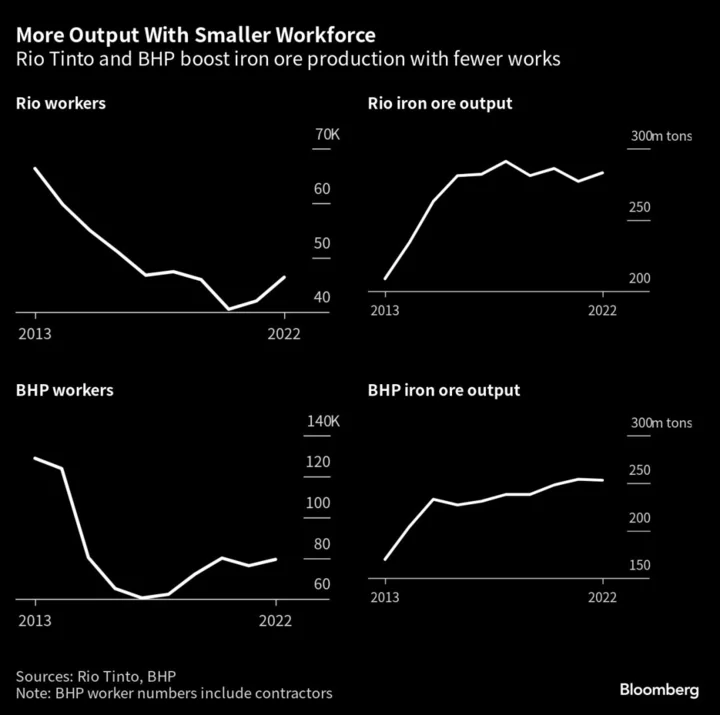
It’s Getting Harder to Find Mining Engineers a Green World Needs
Digging up the metals that go into power grids and electric cars is crucial to the energy transition.
2023-09-01 15:53

Reddit blackout: Why are thousands of the world’s most popular subreddits going dark?
Most of Reddit has now gone “dark” in protest against the management of the online forum. The controversy began when Reddit announced that it would start charging for access to its API, the technology that allows other developers access to its data. Some of those developers immediately announced that the pricing was so high that it would make their apps unsustainable – and one, widely-respected client Apollo, has since said it will have to shut down. That set off outrage across Reddit. While that initially focused on the decision to start charging for access to its data, it has since grown, with many users suggesting that they are generally dissatisfied with the way the site is being managed. What has happened to Reddit? On June 12, many of the world’s biggest subreddits went “dark”. That meant setting their privacy settings to private, so that only anyone who is already a member can see them. For anyone who tries to visit those forums and is not a member – which includes most of those on Reddit, including many of its biggest – they will see a message that it has gone private and is therefore not available. In a widely circulated message explaining the outage, users explained that it was intended as a protest. Some will return on 14 June, after 48 hours of darkness, it says, but others might opt to never come back again if the problem is not addressed. That is because “many moderators aren’t able to put in the work they do with the poor tools available through the official app” the message reads. “This isn’t something any of us do lightly: we do what we do because we love Reddit, and we truly believe this change will make it impossible to keep doing what we love.” Why did Reddit change its policy? All of this began because Reddit announced that it would start charging for access to its API. Many of its users – including Christian Selig, the developer of the Apollo app that is at the centre of much of the controversy – say that this is reasonable. Reddit’s data is used by sites such as Google and to train artificial intelligence systems, for instance. And at the moment, Reddit is not paid for that usage, despite the fact that it costs the company (which is not profitable) to host that data. But it was the pricing and the way it was rolled out that caused such controversy. Mr Selig said that the pricing would cost his app $2 million per month, which is much more than storing the user data is thought to cost Reddit, and he and others were given only 30 days to respond. Which Reddit forums are part of the blackout? Almost all of them. The latest numbers suggest that 7259, out of 7806, of the site’s subreddits are currently unavailable to the public. Of the seven subreddits that have more than 30 million subscribers, all but one – r/pics – have been made private. A full, live list that shows both the subreddits that are down and the overall impact of the protest can be found on this tracking page. How can this happen? Reddit is unusual among social networks in that it depends heavily on its users, who administer the forums and moderate the content that appear on them. That saves it a lot of money – Meta, for instance, spends vast sums on ensuring that problematic content does not appear on Facebook and Instagram – and means that those users feel as if they should be listened to when it comes to such issues. It also means that they are able to take decisions that the management of Reddit might not like them to, including turning those subreddits private. Some 30,000 moderators are thought to be running the subreddits that are involved in the protest, and working together has given them considerable power to grind the site to a halt. Read More Reddit is in chaos – and it’s CEO has finally responded Reddit’s blackout protest is set to continue indefinitely Reddit down amid major protest Popular Reddit app Apollo shuts down as site’s users revolt against it Millions of Reddit users face a blackout over pricing revolt Scientists reveal the ‘violent, catastrophic’ origin of Geminids meteor shower
2023-06-16 00:25

China fines Jack Ma's Ant Group nearly $1 billion
China's top financial regulators have fined Ant Group — the fintech firm founded by billionaire Jack Ma — about 7.1 billion yuan ($994 million) for breaking rules related to consumer protection and corporate governance.
2023-07-07 23:51

The Best Pre-Prime Day Kindle Deals
In a lot of ways, the introduction of the Kindle marked Amazon's transformation into that
2023-06-14 00:29

Get 10TB of cloud storage for life, only $70
TL;DR: As of June 18, get a Lifetime Subscription to Prism Drive Secure Cloud Storage
2023-06-18 17:59

TikTok fined $368 million in Europe for failing to protect children
A major European tech regulator has ordered TikTok to pay a €345 million ($368 million) fine after ruling that the app failed to do enough to protect children.
2023-09-15 23:59

Will There be a Live Event for Fortnite Chapter 4 Season 3?
As of now, there is no confirmed live event for Fortnite Chapter 4 Season 3. It is unlikely Epic Games will produce one to end Fortnite WILDS.
2023-07-26 00:51

Baidu Claims Ernie Bot Outperforms OpenAI's ChatGPT
China's Baidu claims the latest version of its Ernie Bot outperforms OpenAI's ChatGPT. As Bloomberg
2023-06-27 20:19
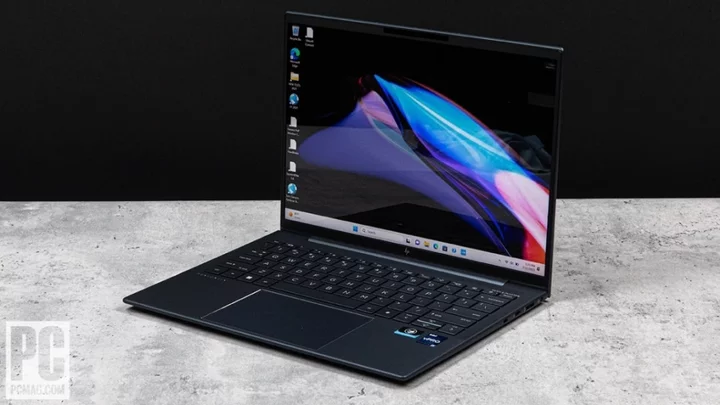

An Impressive Travel Laptop: Living With an HP Dragonfly G4
HP’s Dragonfly G4 is, as the name suggests, the fourth generation of a business laptop
2023-07-29 04:16
You Might Like...

The best dating apps for everyone

Temasek Has No Plans to Invest in Crypto Exchanges For Now: CNBC

Sweepstakes Rules: Readers' Choice Desktop PCs Survey
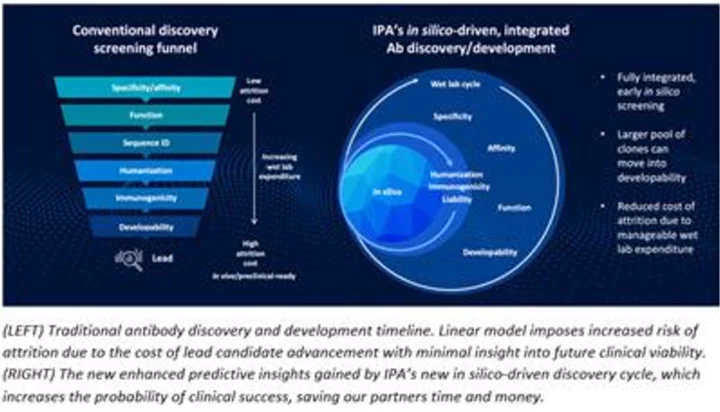
IPA Releases New HYFT-Powered In Silico Humanization Platform, Aims to Disrupt the Transgenic Animal Model Market
Anza Completes Separation from Borrego and Receives New Investment from Energy Capital Partners Led Consortium to Transform Solar and Storage Procurement

USA TODAY NETWORK Ventures Announces 2023 High School Sports Awards Show

Musk's X illegally fired worker challenging office return -US labor board

PowerFlex Enables Large-Scale Fleet Electrification with Intelligent EV Charging Management Software, PowerFlex X
