
Xi’s Micron Ban Shows China’s Limited Options to Hit Back at US
China’s move to ban Micron Technology Inc.’s products marked its most meaningful retaliation yet against US export controls.
2023-05-23 18:30

Ubisoft delays the launch of XDefiant
Ubisoft has announced that it's delaying the launch of 'XDefiant'.
2023-10-12 21:18
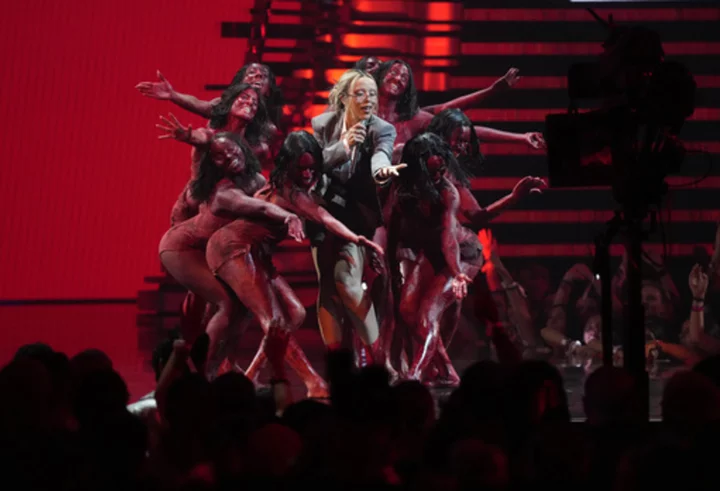

What's streaming now: Doja Cat, 'Sex Education,' 'Spy Kids,' 'The Super Models' and 'Superpower'
This week’s new entertainment releases include an album from Doja Cat, a reboot of Robert Rodriguez’s “Spy Kids” franchise with a film starring Gina Rodriguez and Zachary Levi and the critically-acclaimed “Sex Education,” one of Netflix’s most popular shows, returns for its fourth and final season
2023-09-23 04:20
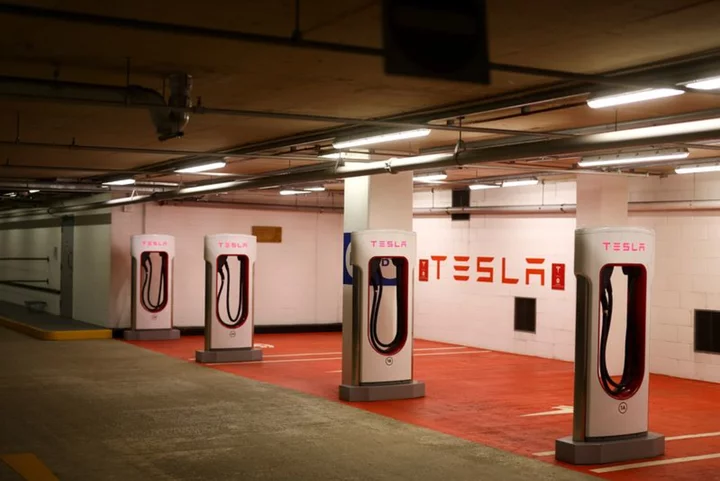

UK petrol station group EG to buy Tesla charging units
LONDON (Reuters) -British petrol station operator EG Group will buy Tesla's ultra-fast charging units to help roll out its electric
2023-11-13 15:58

Obama's first college is latest to end legacy admissions
A California college where President Barack Obama started his undergraduate studies will no longer give special treatment to the children of alumni
2023-07-28 09:56

Google Chrome is getting a redesign. See how it will change.
Google Chrome is celebrating its 15th birthday in style. To celebrate this milestone, Chrome is
2023-09-07 23:49
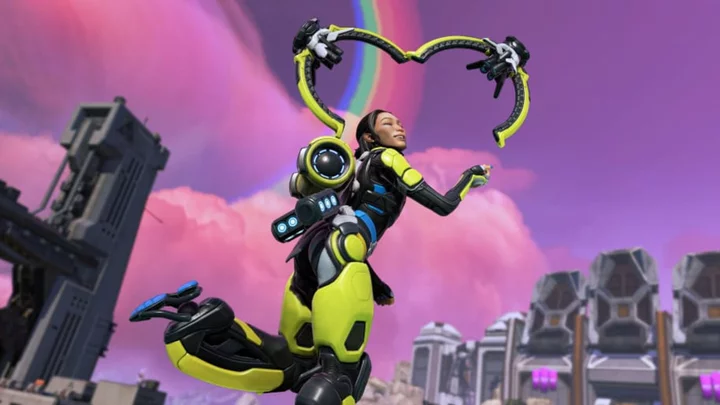

The Most Popular Legends in Apex Legends Season 19
Here's the most popular Legends in Apex Legends 19 based off pick rates for November 2023. Check out which Legend is the best in the game.
2023-11-09 06:28
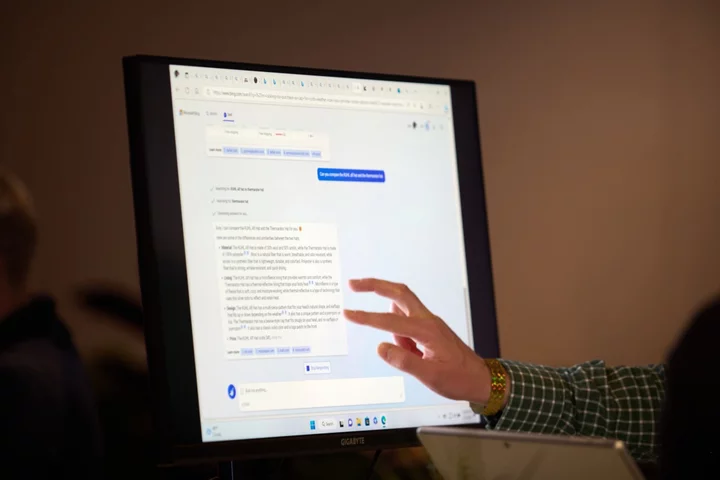
Microsoft Is Bringing OpenAI’s GPT-4 AI model to US Government Agencies
Microsoft Corp. will make it possible for users of its Azure Government cloud computing service, which include a
2023-06-07 21:23
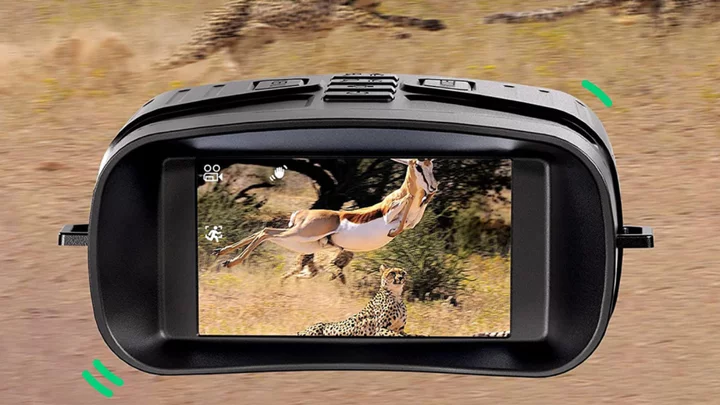

These night vision digital binoculars are on sale for under $100
TL;DR: As of May 14, the Mini Dual Tube Digital Night Vision Binoculars are on
2023-05-14 17:50

CS:GO Major Simulator: Best to Use
CS:GO Major Simulator Majors.im is a great tool to track Swiss round progressions for teams at the BLAST.tv Paris Major 2023.
2023-05-17 00:22
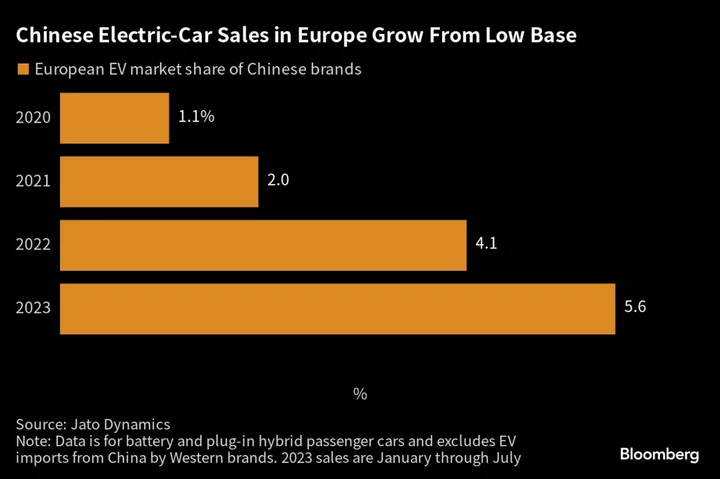
Why Can’t Americans Buy Cheap Chinese EVs?
EV variety is easy to find outside the US. Where American drivers now have about 50 electric cars
2023-09-22 18:53

Google created hurdles to protect smartphone foothold -small search firm
By Diane Bartz WASHINGTON The founder of Branch Metrics, which developed a method of searching within smartphone apps,
2023-09-28 04:27
You Might Like...

Good news for the college class of 2027: It's not too late to get more financial aid

Hestan Wins 2023 Luxe RED Award

Who are Adin Ross' top-tier streamers' picks? Kick star shakes up streaming community with 'GOAT' list, Internet labels it 'disrespectful'

Palantir CEO Touts Power of AI at Customer Conference

OpenAI Loses Third Board Member With Exit of Presidential Candidate Will Hurd

This stacked Amazon Web Services training bundle is on sale for 75% off

SicK: Twitch bans Sentinels' Valorant pro streamer for 'erratic' behavior

Will UFC 5 be on Xbox One?
