
Get a PlayStation 5 bundle for a record-low price
SAVE $60: As of June 7, the PlayStation 5 God of War Ragnarok bundle is
2023-06-07 23:24
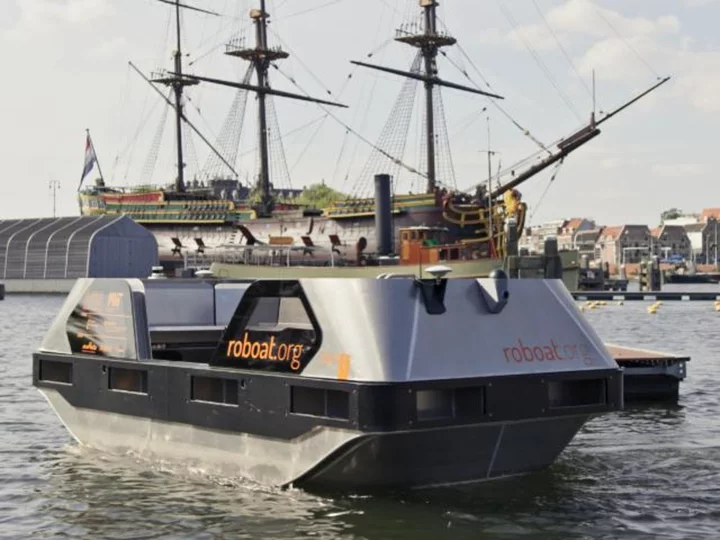

We're still waiting for self-driving cars, but autonomous boats are already here
From cargo ships to passenger ferries, self-driving boats are already making a splash on our waterways.
2023-05-26 16:50

Malaysia to take legal action against Meta, says harmful content not removed
KUALA LUMPUR (Reuters) -Malaysian authorities said on Friday they will take legal action against Facebook parent company Meta Platforms for
2023-06-23 10:53

FTC sues Amazon, alleging it tricked consumers into signing up for Prime
The Federal Trade Commission sued Amazon on Wednesday, alleging that the e-commerce giant has tricked millions of consumers into signing up for its Amazon Prime subscription service through deceptive user interface designs.
2023-06-21 22:52
Analysis-Biden's China tech curbs to keep investors sidelined, fearing more steps
By Kane Wu and Michael Martina HONG KONG/WASHINGTON (Reuters) -President Joe Biden's move to prohibit some U.S. technology investments in
2023-08-10 18:54

Material discovered on Mars would be ’signs of life’ if found on Earth
A Nasa scientist has said chemicals found on Mars would be considered signs of ancient life if they were found on Earth, leading to suggestions the Red Planet could potentially have harboured life. Dr Michelle Thaller said: “On Mars we see chemistry that on Earth, if it were here, we would say is due to life. “But the question is, how well do we understand Mars and are we being fooled by something?” It’s not a done deal, of course. Signs of ancient life that we find regularly on Earth may not mean the same thing elsewhere, particularly with the vastly different conditions between the two planets. Dr Thaller told The Sun she is certain there is life out there in our solar system, but did not reveal the exact chemical substance that had been found. Nasa has previously found methane on Mars, which it said “could have supported ancient life”, and the organisation has also revealed plans to look for amino acids that haven’t yet been destroyed by space radiation. Organic chemicals like amino acids are used by archaeologists to determine whether life was present. A blog post from the US space agency said: “Amino acids can be created by life and by non-biological chemistry. “However, finding certain amino acids on Mars would be considered a potential sign of ancient Martian life because they are widely used by terrestrial life as a component to build proteins. “Proteins are essential to life as they are used to make enzymes which speed up or regulate chemical reactions and to make structures.” Alexander Pavlov of Nasa’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, added: “Our results suggest that amino acids are destroyed by cosmic rays in the Martian surface rocks and regolith at much faster rates than previously thought. “Current Mars rover missions drill down to about two inches (around five centimeters). “At those depths, it would take only 20 million years to destroy amino acids completely.” That may sound like a long time, but Nasa is looking for life that is billions of years old, because scientists think Mars would have been more like Earth back then. Dr Thaller said it was important not to actually say there were signs of life until there is 100 per cent confirmation. “The solar system may be teeming with simple life, microbial life. “We just have to get that 100% certainty to say that we found it and we don’t have that yet.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-27 16:24
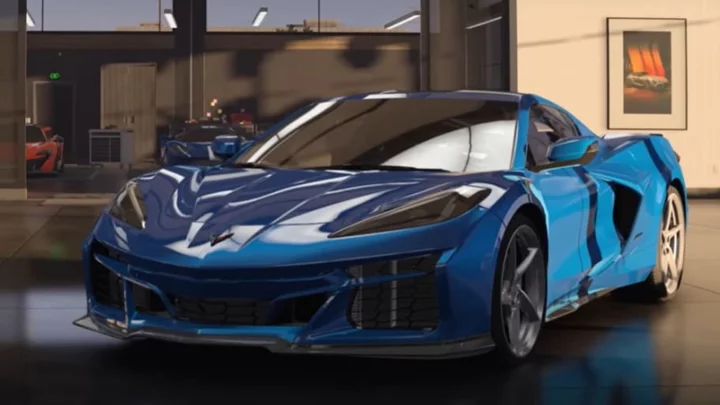

Forza Motorsport Pre-Order Bonuses
Here are the details about the Forza Motorsport Pre-Order Bonuses.
2023-07-26 02:49
Special Olympics Celebrates Third Annual Gaming for Inclusion Initiative
The Special Olympics partnered with Microsoft for the third annual Gaming for Inclusion event featuring notable celebrities such as Xavier Woods, Jamaal Charles and more.
2023-11-23 00:49

Siebert Announces Chairman and CEO Appointment, New Board Member, and Close of Kakao Pay’s $17.4 Million Investment in Siebert
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--May 30, 2023--
2023-05-30 23:16

The iPhone 15 Battery Isn't a Huge Improvement Over Its Predecessor
The iPhone 15 officially made its debut last week and now we know more about
2023-09-17 03:24

Dutch regulator rejects Apple’s objections against fines
AMSTERDAM Dutch competition watchdog ACM on Monday said it had rejected objections by Apple against fines of 50
2023-10-02 15:56

Tech companies including Google gripe about unfair cloud practices
(Reuters) -Technology trade groups as well as Alphabet's Google have griped to the Federal Trade Commission about allegedly unfair business
2023-06-22 08:18
You Might Like...

COP28 Latest: Saudi’s MBS Among Leaders Kicking Off UN Talks

Exclusive-Geely's Zeekr edges closer to US IPO, to make filing public this week - sources
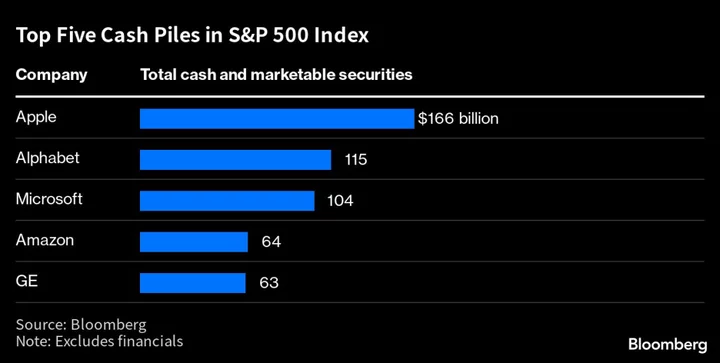
Nasdaq 100’s Big Recovery Faces a Key Tipping Point

FC 24 Champions Rewards Changes: Red Player Picks Removed
Anza Completes Separation from Borrego and Receives New Investment from Energy Capital Partners Led Consortium to Transform Solar and Storage Procurement

Ex-Apple engineer charged with stealing company’s self-driving car technology

AI in music: The top artists are are for and against the technology

Apple reveals price of Vision Pro virtual reality headset as well as release date
