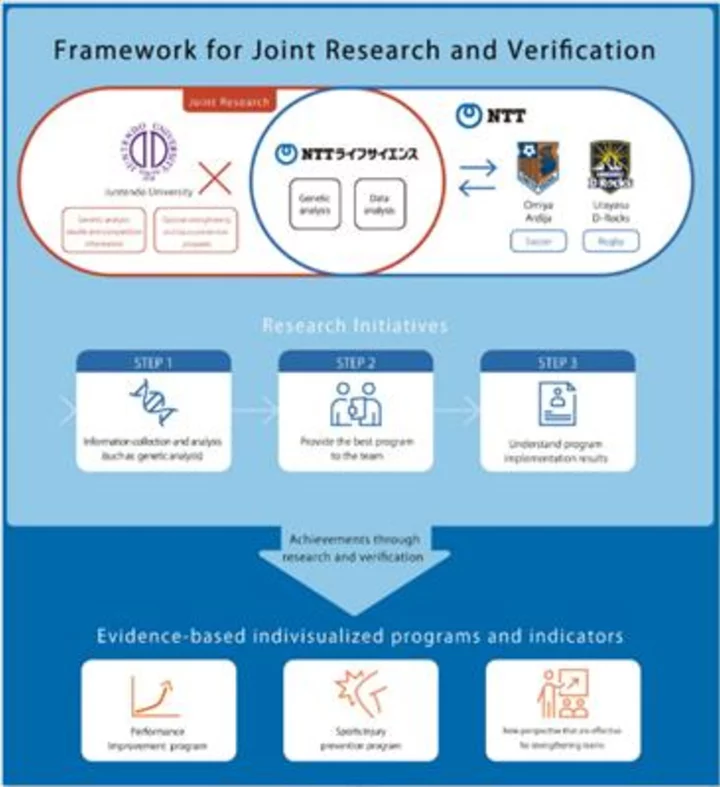
NTT Announces Research Applying Genetic Data to Improve Athletic Performance and Health
TOKYO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Sep 19, 2023--
2023-09-19 20:58

Prime Day Deals so good, they're literally free
There's a big downside to Prime Day deals: even when you spot a great bargain,
2023-07-13 07:24

Should You Free Orpheus in Baldur's Gate 3?
Many Baldur's Gate 3 players aren't sure if they should free Orpheus. Here are some pros and cons for doing so.
2023-08-16 05:59

Man Utd announce new shirt deal with US firm Qualcomm
Manchester United have announced a bumper sponsorship deal with US-based Qualcomm Technologies, whose Snapdragon brand will replace the TeamViewer logo on...
2023-09-13 20:19

South Africa Weighs Environmental Approval for 10 Gigawatts of Power
South Africa’s government is processing applications for projects to produce 9,789 megawatts of renewable energy, the nation’s environment
2023-05-19 18:24

Why Is TV Called the ‘Boob Tube’?
When TVs became popular in the 20th century, some people started calling it ‘the tube.’ That nickname soon spawned an even catchier one: ‘the boob tube.’
2023-07-20 04:21
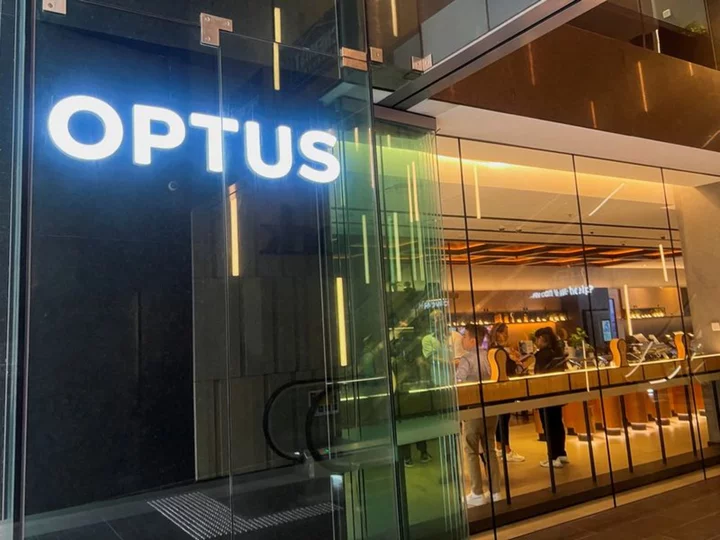

Australia to investigate Optus outage as customers seek compensation
By Renju Jose SYDNEY (Reuters) -Australia said on Thursday it would investigate an outage at telco Optus that cut off
2023-11-09 15:19

How to unblock YouTube for free from anywhere in the world
SAVE 49%: Unblock YouTube from anywhere in the world with ExpressVPN. A one-year subscription to
2023-05-27 11:47

Sanctioned Crypto Mixer Tornado Cash Hijacked By Hackers
Tornado Cash, a service that allows users to mask cryptocurrency transactions, suffered a hostile takeover by hackers through
2023-05-21 18:15

Google to delete millions of Gmail accounts next month in huge purge
Google is set to begin deleting millions of Gmail, Drive and Photos accounts next month as part of a major update to the platform. The purge will impact all personal Google accounts that have been left dormant for at least two years, with emails, documents, spreadsheets, calendar appointments, photos and videos all permanently deleted. The policy was introduced earlier this year but is set to come into effect in December 2023. “We are updating our inactivity policy for Google Accounts to two years across our products,” Ruth Kricheli, Google’s vice president of product management, wrote in a blog post in May. “This update aligns our policy with industry standards around retention and account deletion and also limits the amount of time Google retains your unused personal information.” The move is aimed at protecting active Google users from security threats like phishing scams and account hijacking. Old accounts that have not been used for years are typically at risk from hackers as they may use the same passwords that have been compromised in other security breaches, which are easily available on the dark web. Any account at risk of deletion will receive “multiple notifications” before any action is taken, Google said, including to any associated recovery email addresses. The tech giant has already begun sending emails to those affected, telling users it is “to protect your private information and prevent any unauthorised access to your account even if you’re no longer using our services”. Losing access to a Gmail account could also potentially prevent people from using other online platforms and services that are associated with that email address, even if they are not related to Google. In order to keep an account active and avoid being deleted, Google users are advised to open or send an email, use Google Drive, download an app on the Google Play Store, or simply make a Google Search while logged in to the account. Any account that has posted a video to YouTube will also not be impacted, regardless of when it was last active. Read More ‘Is AI dangerous?’ UK’s most Googled questions about artificial intelligence Big tech poses ‘existential threat’ to UK journalism, survey of editors finds Political ads on Instagram and Facebook can be deepfakes, Meta says
2023-11-08 23:29
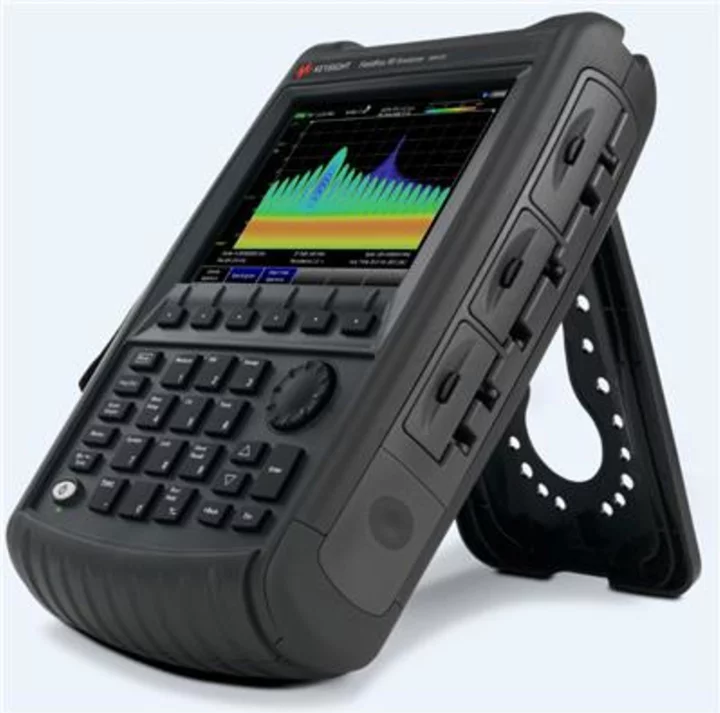

Keysight Introduces Software-Defined Handheld Analyzer
SANTA ROSA, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul 20, 2023--
2023-07-20 23:21
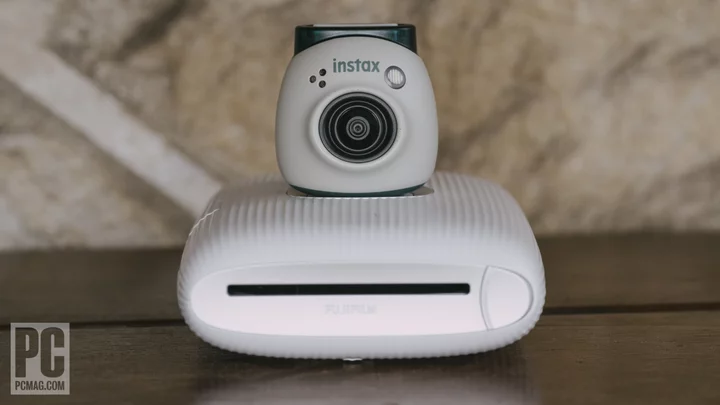

Hands On: Fuji's Instax Pal Earns Points for Cuteness
You've got to hand it to Fujifilm for variety. Just a week after dropping details
2023-09-21 11:18
You Might Like...

Acer Swift Go 16 Review

South Korea’s LG Unveils AI Software for Use Across Its Units

PayRetailers Lands in Bulgaria, Expanding Operations and Establishing Development Hub in Sofia

Mountain Valley Pipeline Builder Asks Supreme Court to Let Work Resume

Matter Adds Three Cybersecurity Brands That Help Organizations Better Protect Themselves Against Global Threats Through Technology, Training and Awareness

Don't miss next week: Jack Harlow on screen, Kesha, Anna Nicole Smith doc and Scott brothers on HGTV

Google will delete inactive accounts this year

Salesforce Touts AI Strategy, Doubles Investment in Startups
